Heterogeneity reduces sensitivity of cell death for TNF-stimuli
- PMID: 22204418
- PMCID: PMC3313907
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-0509-5-204
Heterogeneity reduces sensitivity of cell death for TNF-stimuli
Abstract
Background: Apoptosis is a form of programmed cell death essential for the maintenance of homeostasis and the removal of potentially damaged cells in multicellular organisms. By binding its cognate membrane receptor, TNF receptor type 1 (TNF-R1), the proinflammatory cytokine Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) activates pro-apoptotic signaling via caspase activation, but at the same time also stimulates nuclear factor κB (NF-κB)-mediated survival pathways. Differential dose-response relationships of these two major TNF signaling pathways have been described experimentally and using mathematical modeling. However, the quantitative analysis of the complex interplay between pro- and anti-apoptotic signaling pathways is an open question as it is challenging for several reasons: the overall signaling network is complex, various time scales are present, and cells respond quantitatively and qualitatively in a heterogeneous manner.
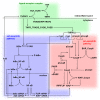
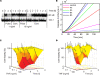
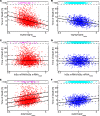
Results: This study analyzes the complex interplay of the crosstalk of TNF-R1 induced pro- and anti-apoptotic signaling pathways based on an experimentally validated mathematical model. The mathematical model describes the temporal responses on both the single cell level as well as the level of a heterogeneous cell population, as observed in the respective quantitative experiments using TNF-R1 stimuli of different strengths and durations. Global sensitivity of the heterogeneous population was quantified by measuring the average gradient of time of death versus each population parameter. This global sensitivity analysis uncovers the concentrations of Caspase-8 and Caspase-3, and their respective inhibitors BAR and XIAP, as key elements for deciding the cell's fate. A simulated knockout of the NF-κB-mediated anti-apoptotic signaling reveals the importance of this pathway for delaying the time of death, reducing the death rate in the case of pulse stimulation and significantly increasing cell-to-cell variability.
Conclusions: Cell ensemble modeling of a heterogeneous cell population including a global sensitivity analysis presented here allowed us to illuminate the role of the different elements and parameters on apoptotic signaling. The receptors serve to transmit the external stimulus; procaspases and their inhibitors control the switching from life to death, while NF-κB enhances the heterogeneity of the cell population. The global sensitivity analysis of the cell population model further revealed an unexpected impact of heterogeneity, i.e. the reduction of parametric sensitivity.
Figures
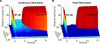
Similar articles
-
Protein Kinase-Mediated Decision Between the Life and Death.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1275:1-33. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-49844-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33539010
-
Ectodomain shedding of TNF receptor 1 induced by protein synthesis inhibitors regulates TNF-alpha-mediated activation of NF-kappaB and caspase-8.Exp Cell Res. 2008 Apr 1;314(6):1406-14. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.01.019. Epub 2008 Feb 6. Exp Cell Res. 2008. PMID: 18289527
-
Cell fate decisions regulated by K63 ubiquitination of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Sep;34(17):3214-28. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00048-14. Epub 2014 Jun 30. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24980434 Free PMC article.
-
Death receptor activation complexes: it takes two to activate TNF receptor 1.Cell Cycle. 2003 Nov-Dec;2(6):550-2. Cell Cycle. 2003. PMID: 14504472 Review.
-
Cellular heterogeneity in TNF/TNFR1 signalling: live cell imaging of cell fate decisions in single cells.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Mar 11;15(3):202. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06559-z. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38467621 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Global analysis of dynamical decision-making models through local computation around the hidden saddle.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33110. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033110. Epub 2012 Mar 15. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22438893 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces a serotonin dependent early increase in ciliary beat frequency and epithelial transport velocity in murine tracheae.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 13;9(3):e91705. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091705. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24626175 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Mechanism of Sinomenii Caulis in Treating Ulcerative Colitis based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024;20(3):195-207. doi: 10.2174/1573409919666230420083102. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024. PMID: 37078344 Free PMC article.
-
Mathematical modeling of the molecular switch of TNFR1-mediated signaling pathways applying Petri net formalism and in silico knockout analysis.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Aug 22;18(8):e1010383. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010383. eCollection 2022 Aug. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 35994517 Free PMC article.
-
Computational analysis of 4-1BB-induced NFκB signaling suggests improvements to CAR cell design.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Aug 26;20(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00937-w. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 36028884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diamantis A, Magiorkinis E, Sakorafas GH, Androutsos G. A brief history of apoptosis: from ancient to modern times. Onkologie. 2008;31:702–706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

