Interordinal chimera formation between medaka and zebrafish for analyzing stem cell differentiation
- PMID: 22204449
- PMCID: PMC3411366
- DOI: 10.1089/scd.2011.0630
Interordinal chimera formation between medaka and zebrafish for analyzing stem cell differentiation
Abstract
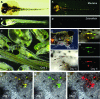
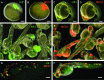
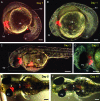
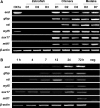
Chimera formation is a standard test for pluripotency of stem cells in vivo. Interspecific chimera formation between distantly related organisms offers also an attractive approach for propagating endangered species. Parameters influencing interspecies chimera formation have remained poorly elucidated. Here, we report interordinal chimera formation between medaka and zebrafish, which separated ∼320 million years ago and exhibit a more than 2-fold difference in developmental speed. We show that, on transplantation into zebrafish blastulae, both noncultivated blastomeres and long-term cultivated embryonic stem (ES) cells of medaka adopted the zebrafish developmental program and differentiated into physiologically functional cell types including pigment cells, blood cells, and cardiomyocytes. We also show that medaka ES cells express differentiation gene markers during chimeric embryogenesis. Therefore, the evolutionary distance and different embryogenesis speeds do not produce donor-host incompatibility to compromise chimera formation between medaka and zebrafish, and molecular markers are valuable for analyzing lineage commitment and cell differentiation in interspecific chimeric embryos.
Figures
References
-
- Evans MJ. Kaufman MH. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature. 1981;292:154–156. - PubMed
-
- Bernemann C. Greber B. Ko K. Sterneckert J. Han DW. Arauzo-Bravo MJ. Scholer HR. Distinct developmental ground states of epiblast stem cell lines determine different pluripotency features. Stem Cells. 2011;29:1496–1503. - PubMed
-
- Reubinoff BE. Pera MF. Fong CY. Trounson A. Bongso A. Embryonic stem cell lines from human blastocysts: somatic differentiation in vitro. Nat Biotechnol. 2000;18:399–404. - PubMed
-
- Hong Y. Winkler C. Schartl M. Pluripotency and differentiation of embryonic stem cell lines from the medakafish (Oryzias latipes) Mech Dev. 1996;60:33–44. - PubMed
-
- Yi M. Hong N. Hong Y. Generation of medaka fish haploid embryonic stem cells. Science. 2009;326:430–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

