Concentration-dependent effects of narciclasine on cell cycle progression in Arabidopsis root tips
- PMID: 22204558
- PMCID: PMC3282671
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-11-184
Concentration-dependent effects of narciclasine on cell cycle progression in Arabidopsis root tips
Abstract
Background: Narciclasine (NCS) is an Amaryllidaceae alkaloid isolated from Narcissus tazetta bulbs. NCS has inhibitory effects on a broad range of biological activities and thus has various potential practical applications. Here we examine how NCS represses plant root growth.
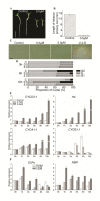
Results: Results showed that the inhibition of NCS on cell division in Arabidopsis root tips and its effects on cell differentiation are concentration-dependent; at low concentrations (0.5 and 1.0 μM) NCS preferentially targets mitotic cell cycle specific/cyclin complexes, whereas at high concentration (5.0 μM) the NCS-stimulated accumulation of Kip-related proteins (KRP1 and RP2) affects the CDK complexes with a role at both G1/S and G2/M phases.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that NCS modulates the coordination between cell division and differentiation in Arabidopsis root tips and hence affects the postembryonic development of Arabidopsis seedlings.
Figures




References
-
- Stevaux O, Dyson NJ. A revised picture of the E2F transcriptional network and RB function. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2002;14:684–691. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

