The Alvarado score for predicting acute appendicitis: a systematic review
- PMID: 22204638
- PMCID: PMC3299622
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7015-9-139
The Alvarado score for predicting acute appendicitis: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: The Alvarado score can be used to stratify patients with symptoms of suspected appendicitis; the validity of the score in certain patient groups and at different cut points is still unclear. The aim of this study was to assess the discrimination (diagnostic accuracy) and calibration performance of the Alvarado score.
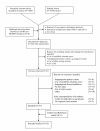
Methods: A systematic search of validation studies in Medline, Embase, DARE and The Cochrane library was performed up to April 2011. We assessed the diagnostic accuracy of the score at the two cut-off points: score of 5 (1 to 4 vs. 5 to 10) and score of 7 (1 to 6 vs. 7 to 10). Calibration was analysed across low (1 to 4), intermediate (5 to 6) and high (7 to 10) risk strata. The analysis focused on three sub-groups: men, women and children.
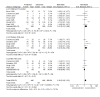
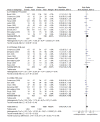
Results: Forty-two studies were included in the review. In terms of diagnostic accuracy, the cut-point of 5 was good at 'ruling out' admission for appendicitis (sensitivity 99% overall, 96% men, 99% woman, 99% children). At the cut-point of 7, recommended for 'ruling in' appendicitis and progression to surgery, the score performed poorly in each subgroup (specificity overall 81%, men 57%, woman 73%, children 76%). The Alvarado score is well calibrated in men across all risk strata (low RR 1.06, 95% CI 0.87 to 1.28; intermediate 1.09, 0.86 to 1.37 and high 1.02, 0.97 to 1.08). The score over-predicts the probability of appendicitis in children in the intermediate and high risk groups and in women across all risk strata.
Conclusions: The Alvarado score is a useful diagnostic 'rule out' score at a cut point of 5 for all patient groups. The score is well calibrated in men, inconsistent in children and over-predicts the probability of appendicitis in women across all strata of risk.
Figures



References
-
- Ergul E. Importance of family history and genetics for the prediction of acute appendicitis. Internet J Surg. 2007;10:2.
-
- Reilly BM, Evans AT. Translating clinical research into clinical practice: impact of using prediction rules to make decisions. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144:201–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

