Mineralocorticoid receptor blocker eplerenone improves endothelial function and inhibits Rho-associated kinase activity in patients with hypertension
- PMID: 22205191
- PMCID: PMC6444052
- DOI: 10.1038/clpt.2011.227
Mineralocorticoid receptor blocker eplerenone improves endothelial function and inhibits Rho-associated kinase activity in patients with hypertension
Abstract
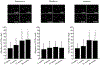
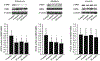
Hypertension is associated with endothelial dysfunction and activated Rho-associated kinases (ROCKs). The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of the selective mineralocorticoid receptor blocker, eplerenone, on endothelial function and ROCK activity in patients with hypertension. The study was carried out over 48 weeks in 60 untreated patients with hypertension who were randomly assigned to eplerenone, nifedipine, and losartan groups. We evaluated the effects of each treatment on flow-mediated vasodilation (FMD) and ROCK activity in peripheral leukocytes. Eplerenone increased FMD and decreased leukocyte ROCK activity. Nifedipine decreased ROCK activity but did not alter FMD. Losartan increased FMD but did not alter ROCK activity. Hypotensive effects were similar in the three groups, as was nitroglycerin-induced vasodilation during the follow-up period. There were no significant differences between the groups with respect to other parameters. The study results show that eplerenone improves endothelial function and inhibits ROCK activity in patients with essential hypertension.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
J.K.L. is a consultant for Asahi-Kasei Pharmaceutical, Inc. The other authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Eplerenone improves endothelial function and arterial stiffness and inhibits Rho-associated kinase activity in patients with idiopathic hyperaldosteronism: a pilot study.J Hypertens. 2019 May;37(5):1083-1095. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001989. J Hypertens. 2019. PMID: 30418321 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium channel blocker and Rho-associated kinase activity in patients with hypertension.J Hypertens. 2011 Feb;29(2):373-9. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e328340902d. J Hypertens. 2011. PMID: 21063203 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Beneficial effect of T-type calcium channel blockers on endothelial function in patients with essential hypertension.Hypertens Res. 2005 Nov;28(11):889-94. doi: 10.1291/hypres.28.889. Hypertens Res. 2005. PMID: 16555577 Clinical Trial.
-
Eplerenone: a selective aldosterone blocker.Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2003 Fall;21(3):169-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3466.2003.tb00114.x. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2003. PMID: 12931252 Review.
-
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists and endothelial function.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2008 Sep;9(9):963-9. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18729003 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Eplerenone improves endothelial function and arterial stiffness and inhibits Rho-associated kinase activity in patients with idiopathic hyperaldosteronism: a pilot study.J Hypertens. 2019 May;37(5):1083-1095. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001989. J Hypertens. 2019. PMID: 30418321 Free PMC article.
-
Which diuretic for which hypertensive patient?Indian Heart J. 2017 Mar-Apr;69(2):282-283. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2017.02.012. Epub 2017 Mar 3. Indian Heart J. 2017. PMID: 28460779 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Hyperuricemia is independently associated with endothelial dysfunction in postmenopausal women but not in premenopausal women.BMJ Open. 2013 Nov 8;3(11):e003659. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003659. BMJ Open. 2013. PMID: 24213096 Free PMC article.
-
Rho kinase cascade activation in circulating leukocytes in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 May 6;19(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01027-2. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32375786 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular risk in patients receiving antihypertensive drug treatment from the perspective of endothelial function.Hypertens Res. 2022 Aug;45(8):1322-1333. doi: 10.1038/s41440-022-00936-x. Epub 2022 May 20. Hypertens Res. 2022. PMID: 35595983 Review.
References
-
- Amano M et al. Formation of actin stress fibers and focal adhesions enhanced by Rho-kinase. Science 275, 1308–1311 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Uehata M et al. Calcium sensitization of smooth muscle mediated by a Rho-associated protein kinase in hypertension. Nature 389, 990–994 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Hall A Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science 279, 509–514 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Kimura K et al. Regulation of the association of adducin with actin filaments by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) and myosin phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem 273, 5542–5548 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Sauzeau V et al. Cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase signaling pathway inhibits RhoA-induced Ca2+ sensitization of contraction in vascular smooth muscle. J. Biol. Chem 275, 21722–21729 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

