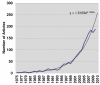
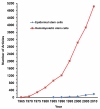
25 years of epidermal stem cell research
- PMID: 22205306
- PMCID: PMC3998762
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2011.434
25 years of epidermal stem cell research
Abstract
This is a chronicle of concepts in the field of epidermal stem cell biology and a historic look at their development over time. The past 25 years have seen the evolution of epidermal stem cell science, from first fundamental studies to a sophisticated science. The study of epithelial stem cell biology was aided by the ability to visualize the distribution of stem cells and their progeny through lineage analysis studies. The excellent progress we have made in understanding epidermal stem cell biology is discussed in this article. The challenges we still face in understanding epidermal stem cells include defining molecular markers for stem and progenitor sub-populations, determining the locations and contributions of the different stem cell niches, and mapping regulatory pathways of epidermal stem cell proliferation and differentiation. However, our rapidly evolving understanding of epidermal stem cells has many potential uses that promise to translate into improved patient therapy.
Figures
Comment in
-
Interfollicular epidermal homeostasis: a response to Ghadially, '25 years of epidermal stem cell research'.J Invest Dermatol. 2012 Aug;132(8):2096-7. doi: 10.1038/jid.2012.122. Epub 2012 Apr 19. J Invest Dermatol. 2012. PMID: 22513783 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Interfollicular epidermal homeostasis: a response to Ghadially, '25 years of epidermal stem cell research'.J Invest Dermatol. 2012 Aug;132(8):2096-7. doi: 10.1038/jid.2012.122. Epub 2012 Apr 19. J Invest Dermatol. 2012. PMID: 22513783 No abstract available.
-
[Historical review of reprogramming and pluripotent stem cell research in China].Yi Chuan. 2018 Oct 20;40(10):825-840. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.18-209. Yi Chuan. 2018. PMID: 30369467 Review. Chinese.
-
20 Years of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Research: It All Started with Five Lines.Cell Stem Cell. 2018 Nov 1;23(5):644-648. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.10.009. Cell Stem Cell. 2018. PMID: 30388422
-
[From Gurdon to Yamanaka--a brief history of cell reprogramming].Postepy Biochem. 2013;59(2):124-30. Postepy Biochem. 2013. PMID: 24044277 Polish.
-
Fifty years of cell biology in The Journal of Investigative Dermatology.J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Apr;92(4 Suppl):105S-112S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep13075087. J Invest Dermatol. 1989. PMID: 2649600 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Esophageal human β-defensin expression in eosinophilic esophagitis.Pediatr Res. 2013 May;73(5):647-54. doi: 10.1038/pr.2013.23. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Pediatr Res. 2013. PMID: 23385963 Free PMC article.
-
Dental Pulp-Derived Stem Cells Reduce Inflammation, Accelerate Wound Healing and Mediate M2 Polarization of Myeloid Cells.Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 17;10(8):1999. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081999. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36009546 Free PMC article.
-
Deregulation of epidermal stem cell niche contributes to pathogenesis of nonhealing venous ulcers.Wound Repair Regen. 2014 Mar-Apr;22(2):220-227. doi: 10.1111/wrr.12142. Wound Repair Regen. 2014. PMID: 24635172 Free PMC article.
-
The carboxy-terminus of p63 links cell cycle control and the proliferative potential of epidermal progenitor cells.Development. 2015 Jan 15;142(2):282-90. doi: 10.1242/dev.118307. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Development. 2015. PMID: 25503409 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into skin cell-based osteogenesis: a review.F1000Res. 2017 Mar 17;6:291. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.10280.1. eCollection 2017. F1000Res. 2017. PMID: 28413622 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aasen T, Raya A, Barrero MJ, et al. Efficient and rapid generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human keratinocytes. Nat Biotech. 2008 Nov;26(11):1276–1284. - PubMed
-
- Akashi K, Traver D, Miyamoto T, et al. A clonogenic common myeloid progenitor that gives rise to all myeloid lineages. Nature. 2000 Mar 9;404(6774):193–197. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong L, Stojkovic M, Dimmick I, et al. Phenotypic characterization of murine primitive hematopoietic progenitor cells isolated on basis of aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. Stem Cells (Dayton, Ohio) 2004;22(7):1142–1151. - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Matsuno K, Fortini ME. Notch signaling. Science (New York, N.Y.) 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):225–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous