Synaptic pathways that shape the excitatory drive in an OFF retinal ganglion cell
- PMID: 22205648
- PMCID: PMC3331668
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00924.2011
Synaptic pathways that shape the excitatory drive in an OFF retinal ganglion cell
Abstract
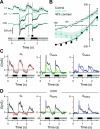
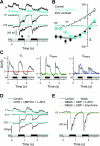
Different types of retinal ganglion cells represent distinct spatiotemporal filters that respond selectively to specific features in the visual input. Much about the circuitry and synaptic mechanisms that underlie such specificity remains to be determined. This study examines how N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor signaling combines with other excitatory and inhibitory mechanisms to shape the output of small-field OFF brisk-sustained ganglion cells (OFF-BSGCs) in the rabbit retina. We used voltage clamp to separately resolve NMDA, α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA), and inhibitory inputs elicited by stimulation of the receptive field center. Three converging circuits were identified. First is a direct glutamatergic input, arising from OFF cone bipolar cells (CBCs), which is mediated by synaptic NMDA and AMPA receptors. The NMDA input was saturated at 10% contrast, whereas the AMPA input increased monotonically up to 60% contrast. We propose that NMDA inputs selectively enhance sensitivity to low contrasts. The OFF bipolar cells, mediating this direct excitatory input, express dendritic kainate (KA) receptors, which are resistant to the nonselective AMPA/KA receptor antagonist, 2,3-dioxo-6-nitro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo[f]quinoxaline-7-sulfonamide disodium salt (NBQX), but are suppressed by a GluK1- and GluK3-selective antagonist, (S)-1-(2-amino-2-carboxyethyl)-3-(2-carboxy-thiophene-3-yl-methyl)-5-methylpyrimidine-2,4-dione (UBP-310). The second circuit entails glycinergic crossover inhibition, arising from ON-CBCs and mediated by AII amacrine cells, which modulate glutamate release from the OFF-CBC terminals. The third circuit also comprises glycinergic crossover inhibition, which is driven by the ON pathway; however, this inhibition impinges directly on the OFF-BSGCs and is mediated by an unknown glycinergic amacrine cell that expresses AMPA but not KA receptors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Synaptic and Morphological Basis of Orientation Selectivity in a Polyaxonal Amacrine Cell of the Rabbit Retina.J Neurosci. 2015 Sep 30;35(39):13336-50. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1712-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26424882 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Mechanisms Generating Orientation Selectivity in the ON Pathway of the Rabbit Retina.J Neurosci. 2016 Mar 16;36(11):3336-49. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1432-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26985041 Free PMC article.
-
The network-selective actions of quinoxalines on the neurocircuitry operations of the rabbit retina.Brain Res. 1999 Jun 12;831(1-2):206-28. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(99)01448-1. Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10412000
-
Distinct synaptic mechanisms create parallel S-ON and S-OFF color opponent pathways in the primate retina.Vis Neurosci. 2014 Mar;31(2):139-51. doi: 10.1017/S0952523813000230. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Vis Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 23895762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of AMPA and NMDA receptors to excitatory responses in the inferior colliculus.Hear Res. 2002 Jun;168(1-2):35-42. doi: 10.1016/s0378-5955(02)00372-6. Hear Res. 2002. PMID: 12117507 Review.
Cited by
-
Alterations in Kainate Receptor and TRPM1 Localization in Bipolar Cells after Retinal Photoreceptor Degeneration.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Dec 22;9:486. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00486. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26733812 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory input to the direction-selective ganglion cell is saturated at low contrast.J Neurophysiol. 2015 Aug;114(2):927-41. doi: 10.1152/jn.00413.2015. Epub 2015 Jun 10. J Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 26063782 Free PMC article.
-
APLP2 Regulates Refractive Error and Myopia Development in Mice and Humans.PLoS Genet. 2015 Aug 27;11(8):e1005432. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005432. eCollection 2015 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26313004 Free PMC article.
-
Essential Roles of Tbr1 in the Formation and Maintenance of the Orientation-Selective J-RGCs and a Group of OFF-Sustained RGCs in Mouse.Cell Rep. 2019 Apr 16;27(3):900-915.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.03.077. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 30995485 Free PMC article.
-
Kainate receptor subunit diversity underlying response diversity in retinal off bipolar cells.J Physiol. 2014 Apr 1;592(7):1457-77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.265033. Epub 2014 Jan 6. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24396054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alt A, Weiss B, Ogden AM, Knauss JL, Oler J, Ho K, Large TH, Bleakman D. Pharmacological characterization of glutamatergic agonists and antagonists at recombinant human homomeric and heteromeric kainate receptors in vitro. Neuropharmacology 46: 793–806, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Amthor FR, Takahashi ES, Oyster CW. Morphologies of rabbit retinal ganglion cells with concentric receptive fields. J Comp Neurol 280: 72–96, 1989 - PubMed
-
- Berretta N, Jones RS. Tonic facilitation of glutamate release by presynaptic N-methyl-d-aspartate autoreceptors in the entorhinal cortex. Neuroscience 75: 339–344, 1996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

