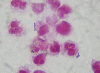
Recurrent urinary infection with Bifidobacterium scardovii
- PMID: 22205811
- PMCID: PMC3295111
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.06027-11
Recurrent urinary infection with Bifidobacterium scardovii
Abstract
Bifidobacterium species are difficult to identify and may be underreported or not recovered by many laboratories because of their slow growth. We emphasize the importance of the Gram stain in urine samples and the addition of enriched media and enhanced atmosphere over time for urine cultures with pyuria. This is the first report of a Bifidobacterium scardovii recurrent urinary infection in an elderly woman.
Figures
References
-
- Felis G, Dellaglio F. 2007. Taxonomy of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria. Curr. Issues Intest. Microbiol. 8:44–61 - PubMed
-
- Funke G, Bernard KA. 2011. Coryneform gram-positive rods, p 413–442 In Versalovic J, et al. (ed), Manual of clinical microbiology, 10th ed, vol 1 ASM Press, Washington, DC
-
- Hoyles L. 2002. Bifidobacterium scardovii sp. nov., from human sources. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 52:995–999 - PubMed
-
- Limansky A, Viale A. 2002. Can composition and structural features of oligonucleotides contribute to their wide scale applicability as random PCR primers in mapping bacterial genome diversity? J. Microbiol. Methods 50:391–397 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases