Use of illumina deep sequencing technology to differentiate hepatitis C virus variants
- PMID: 22205816
- PMCID: PMC3295113
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.05715-11
Use of illumina deep sequencing technology to differentiate hepatitis C virus variants
Abstract
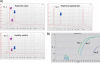
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a positive-strand enveloped RNA virus that shows diverse viral populations even in one individual. Though Sanger sequencing has been used to determine viral sequences, deep sequencing technologies are much faster and can perform large-scale sequencing. We demonstrate the successful use of Illumina deep sequencing technology and subsequent analyses to determine the genetic variants and amino acid substitutions in both treatment-naïve (patient 1) and treatment-experienced (patient 7) isolates from HCV-infected patients. As a result, almost the full nucleotide sequence of HCV was detectable for patients 1 and 7. The reads were mapped to the HCV reference sequence. The coverage was 99.8% and the average depth was 69.5× for patient 7, with values of 99.4% (coverage) and 51.1× (average depth) for patient 1. In patient 7, amino acid (aa) 70 in the core region showed arginine, with methionine at aa 91, by Sanger sequencing. Major variants showed the same amino acid sequence, but minor variants were detectable in 18% (6/34 sequences) of sequences, with replacement of methionine by leucine at aa 91. In NS3, 8 amino acid positions showed mixed variants (T72T/I, K213K/R, G237G/S, P264P/S/A, S297S/A, A358A/T, S457S/C, and I615I/M) in patient 7. In patient 1, 3 amino acid positions showed mixed variants (L14L/F/V, S61S/A, and I586T/I). In conclusion, deep sequencing technologies are powerful tools for obtaining more profound insight into the dynamics of variants in the HCV quasispecies in human serum.
Figures


References
-
- Akuta N, et al. 2007. Prediction of response to pegylated interferon and ribavirin in hepatitis C by polymorphisms in the viral core protein and very early dynamics of viremia. Intervirology 50:361–368 - PubMed
-
- Akuta N, et al. 2005. Association of amino acid substitution pattern in core protein of hepatitis C virus genotype 1b high viral load and non-virological response to interferon-ribavirin combination therapy. Intervirology 48:372–380 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

