ZnO-based amperometric enzyme biosensors
- PMID: 22205864
- PMCID: PMC3244010
- DOI: 10.3390/s100201216
ZnO-based amperometric enzyme biosensors
Abstract
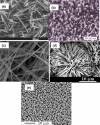
Nanostructured ZnO with its unique properties could provide a suitable microenvironment for immobilization of enzymes while retaining their biological activity, and thus lead to an expanded use of this nanomaterial for the construction of electrochemical biosensors with enhanced analytical performance. ZnO-based enzyme electrochemical biosensors are summarized in several tables for an easy overview according to the target biosensing analyte (glucose, hydrogen peroxide, phenol and cholesterol), respectively. Moreover, recent developments in enzyme electrochemical biosensors based on ZnO nanomaterials are reviewed with an emphasis on the fabrications and features of ZnO, approaches for biosensor construction (e.g., modified electrodes and enzyme immobilization) and biosensor performances.
Keywords: ZnO; electrochemical; enzyme biosensors.
Figures
References
-
- Dzyadevych S.V., Arkhypova V.N., Soldatkin A.P., El'skaya A.V., Martelet C., Jaffrezic-Renault N. Amperometric enzyme biosensors: Past, present and future. IRBM. 2008;29:171–180.
-
- Wang J. Electroanalysis and biosensors. Anal. Chem. 1995;67:487–492. - PubMed
-
- Burmeister J.J., Gerhardt G.A. Self referencing ceramic based multisite microelectrodes for the detection and elimination of interferences from the measurement of L-glutamate and other analytes. Anal. Chem. 2001;73:1037–1042. - PubMed
-
- Norton D.P., Heo Y.W., Ivill M.P., Pearton S.J., Chisholm M.F., Steiner T. ZnO: growth, doping & processing. Mater. Today. 2004;7:34–40.
-
- Sun X.W., Kwok H.S. Optical properties of epitaxially grown zinc oxide films on sapphire by pulsed laser deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 1999;86:408–411.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

