Impact of immunization technology and assay application on antibody performance--a systematic comparative evaluation
- PMID: 22205963
- PMCID: PMC3243671
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028718
Impact of immunization technology and assay application on antibody performance--a systematic comparative evaluation
Abstract
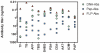
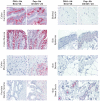
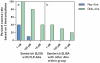
Antibodies are quintessential affinity reagents for the investigation and determination of a protein's expression patterns, localization, quantitation, modifications, purification, and functional understanding. Antibodies are typically used in techniques such as Western blot, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), among others. The methods employed to generate antibodies can have a profound impact on their success in any of these applications. We raised antibodies against 10 serum proteins using 3 immunization methods: peptide antigens (3 per protein), DNA prime/protein fragment-boost ("DNA immunization"; 3 per protein), and full length protein. Antibodies thus generated were systematically evaluated using several different assay technologies (ELISA, IHC, and Western blot). Antibodies raised against peptides worked predominantly in applications where the target protein was denatured (57% success in Western blot, 66% success in immunohistochemistry), although 37% of the antibodies thus generated did not work in any of these applications. In contrast, antibodies produced by DNA immunization performed well against both denatured and native targets with a high level of success: 93% success in Western blots, 100% success in immunohistochemistry, and 79% success in ELISA. Importantly, success in one assay method was not predictive of success in another. Immunization with full length protein consistently yielded the best results; however, this method is not typically available for new targets, due to the difficulty of generating full length protein. We conclude that DNA immunization strategies which are not encumbered by the limitations of efficacy (peptides) or requirements for full length proteins can be quite successful, particularly when multiple constructs for each protein are used.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Anti-peptide monoclonal antibodies generated for immuno-multiple reaction monitoring-mass spectrometry assays have a high probability of supporting Western blot and ELISA.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015 Feb;14(2):382-98. doi: 10.1074/mcp.O114.043133. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25512614 Free PMC article.
-
Antibodies raised against synthetic peptides react with choline acetyltransferase in various immunoassays and in immunohistochemistry.J Neurochem. 1993 Sep;61(3):804-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03590.x. J Neurochem. 1993. PMID: 8360685
-
A novel system for the efficient generation of antibodies following immunization of unique knockout mouse strains.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 23;5(9):e12892. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012892. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20886120 Free PMC article.
-
Production and characterization of peptide antibodies.Methods. 2012 Feb;56(2):136-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2011.12.001. Epub 2011 Dec 8. Methods. 2012. PMID: 22178691 Review.
-
Why recombinant antibodies - benefits and applications.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2019 Dec;60:153-158. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2019.01.012. Epub 2019 Mar 5. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30849700 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Cross-Talk between Gravity- and Light-Sensing Mechanisms in Euglena gracilis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 3;23(5):2776. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052776. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269918 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of state-dependent monoclonal antibodies against the 12-transmembrane domain glucose transporter 4 using virus-like particles.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 May 29;115(22):E4990-E4999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1716788115. Epub 2018 May 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29769329 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale 3-dimensional quantitative imaging of tissues: state-of-the-art and translational implications.Transl Res. 2017 Nov;189:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2017.07.006. Epub 2017 Jul 22. Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 28784428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunological detection of AcAMP antimicrobial peptide secreted by Aspergillus clavatus.Iran J Microbiol. 2021 Apr;13(2):235-242. doi: 10.18502/ijm.v13i2.5985. Iran J Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34540159 Free PMC article.
-
The v8-10 variant isoform of CD44 is selectively expressed in the normal human colonic stem cell niche and frequently is overexpressed in colon carcinomas during tumor development.Cancer Biol Ther. 2023 Dec 31;24(1):2195363. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2023.2195363. Cancer Biol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37005380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amin DN, Hida K, Bielenberg DR, Klagsbrun M. Tumor endothelial cells express epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) but not ErbB3 and are responsive to EGF and to EGFR kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2006;66:2173–2180. - PubMed
-
- Garcia JF, Garcia JF, Maestre L, Lucas E, Sanchez-Verde L, et al. Genetic immunization: A new monoclonal antibody for the detection of BCL-6 protein in paraffin sections. Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry. 2006;54(1):31–38. - PubMed
-
- Haab BB. Antibody arrays in cancer research. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 2005;4(4):377–383. - PubMed
-
- Li HH, Zhou G, Xiao-Bing F, Zhang L. Antigen expression in human endocrine sweat glands. Journal of Cutaneous Pathology. 2009;36:318–324. - PubMed
-
- Schwenk JM, Lindberg J, Sundberg M, Uhlen M, Nilson P. Determination of binding specificities in highly multiplexed bead-based assays for antibody proteomics. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 2007;6(1):125–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

