Employing machine learning for reliable miRNA target identification in plants
- PMID: 22206472
- PMCID: PMC3293931
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-636
Employing machine learning for reliable miRNA target identification in plants
Abstract
Background: miRNAs are ~21 nucleotide long small noncoding RNA molecules, formed endogenously in most of the eukaryotes, which mainly control their target genes post transcriptionally by interacting and silencing them. While a lot of tools has been developed for animal miRNA target system, plant miRNA target identification system has witnessed limited development. Most of them have been centered around exact complementarity match. Very few of them considered other factors like multiple target sites and role of flanking regions.
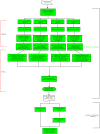
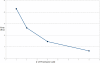
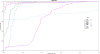
Result: In the present work, a Support Vector Regression (SVR) approach has been implemented for plant miRNA target identification, utilizing position specific dinucleotide density variation information around the target sites, to yield highly reliable result. It has been named as p-TAREF (plant-Target Refiner). Performance comparison for p-TAREF was done with other prediction tools for plants with utmost rigor and where p-TAREF was found better performing in several aspects. Further, p-TAREF was run over the experimentally validated miRNA targets from species like Arabidopsis, Medicago, Rice and Tomato, and detected them accurately, suggesting gross usability of p-TAREF for plant species. Using p-TAREF, target identification was done for the complete Rice transcriptome, supported by expression and degradome based data. miR156 was found as an important component of the Rice regulatory system, where control of genes associated with growth and transcription looked predominant. The entire methodology has been implemented in a multi-threaded parallel architecture in Java, to enable fast processing for web-server version as well as standalone version. This also makes it to run even on a simple desktop computer in concurrent mode. It also provides a facility to gather experimental support for predictions made, through on the spot expression data analysis, in its web-server version.
Conclusion: A machine learning multivariate feature tool has been implemented in parallel and locally installable form, for plant miRNA target identification. The performance was assessed and compared through comprehensive testing and benchmarking, suggesting a reliable performance and gross usability for transcriptome wide plant miRNA target identification.
Figures



Similar articles
-
PMRD: plant microRNA database.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jan;38(Database issue):D806-13. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp818. Epub 2009 Oct 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 19808935 Free PMC article.
-
miR-BAG: bagging based identification of microRNA precursors.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45782. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045782. Epub 2012 Sep 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23049860 Free PMC article.
-
Plant microRNA-target interaction identification model based on the integration of prediction tools and support vector machine.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 22;9(7):e103181. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103181. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25051153 Free PMC article.
-
A reversed framework for the identification of microRNA-target pairs in plants.Brief Bioinform. 2013 May;14(3):293-301. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbs040. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Brief Bioinform. 2013. PMID: 22811545 Review.
-
The use of high-throughput sequencing methods for plant microRNA research.RNA Biol. 2015;12(7):709-19. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1053686. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 26016494 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plant Regulomics Portal (PRP): a comprehensive integrated regulatory information and analysis portal for plant genomes.Database (Oxford). 2019 Jan 1;2019:baz130. doi: 10.1093/database/baz130. Database (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 31796964 Free PMC article.
-
Rice Improvement Through Genome-Based Functional Analysis and Molecular Breeding in India.Rice (N Y). 2016 Dec;9(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12284-015-0073-2. Epub 2016 Jan 7. Rice (N Y). 2016. PMID: 26743769 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of performance of plant miRNA target prediction tools and the characterization of features for genome-wide target prediction.BMC Genomics. 2014 May 8;15(1):348. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-348. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24885295 Free PMC article.
-
ptRNApred: computational identification and classification of post-transcriptional RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Dec 16;42(22):e167. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku918. Epub 2014 Oct 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25303994 Free PMC article.
-
GeneAI 3.0: powerful, novel, generalized hybrid and ensemble deep learning frameworks for miRNA species classification of stationary patterns from nucleotides.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 26;14(1):7154. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56786-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38531923 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

