Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of potent quinoline and pyrroloquinoline ammosamide analogues as inhibitors of quinone reductase 2
- PMID: 22206487
- PMCID: PMC3262027
- DOI: 10.1021/jm201251c
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of potent quinoline and pyrroloquinoline ammosamide analogues as inhibitors of quinone reductase 2
Abstract
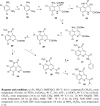
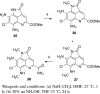
A variety of ammosamide B analogues have been synthesized and evaluated as inhibitors of quinone reductase 2 (QR2). The potencies of the resulting series of QR2 inhibitors range from 4.1 to 25,200 nM. The data provide insight into the structural parameters necessary for QR2 inhibitory activity. The natural product ammosamide B proved to be a potent QR2 inhibitor, and the potencies of the analogues generally decreased as their structures became more distinct from that of ammosamide B. Methylation of the 8-amino group of ammosamide B was an exception, resulting in an increase in quinone reductase 2 inhibitory activity from an IC(50) of 61 nM to IC(50) 4.1 nM.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A tandem Friedel-Crafts based method for the construction of a tricyclic pyrroloquinoline skeleton and its application in the synthesis of ammosamide B.Chem Commun (Camb). 2013 Jul 25;49(58):6519-21. doi: 10.1039/c3cc42463d. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Chem Commun (Camb). 2013. PMID: 23764772
-
Synthesis of casimiroin and optimization of its quinone reductase 2 and aromatase inhibitory activities.J Med Chem. 2009 Apr 9;52(7):1873-84. doi: 10.1021/jm801335z. J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19265439 Free PMC article.
-
Thiol-Based Probe for Electrophilic Natural Products Reveals That Most of the Ammosamides Are Artifacts.J Nat Prod. 2017 Jan 27;80(1):126-133. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00773. Epub 2017 Jan 5. J Nat Prod. 2017. PMID: 28055208
-
Synthesis, biological activity, and quantitative structure-activity relationship study of azanaphthalimide and arylnaphthalimide derivatives.J Med Chem. 2004 Apr 22;47(9):2236-42. doi: 10.1021/jm0310784. J Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15084122
-
Synthesis and antitumor characterization of pyrazolic analogues of the marine pyrroloquinoline alkaloids: wakayin and tsitsikammamines.J Med Chem. 2006 May 18;49(10):2979-88. doi: 10.1021/jm051247f. J Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16686539
Cited by
-
Role of Quinone Reductase 2 in the Antimalarial Properties of Indolone-Type Derivatives.Molecules. 2017 Jan 30;22(2):210. doi: 10.3390/molecules22020210. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28146103 Free PMC article.
-
Unexpected Transformations during Pyrroloiminoquinone Biosynthesis.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 May 22;146(20):14235-14245. doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c03677. Epub 2024 May 8. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 38719200 Free PMC article.
-
Practical, scalable, and transition metal-free visible light-induced heteroarylation route to substituted oxindoles.Chem Sci. 2023 Jan 3;14(4):897-902. doi: 10.1039/d2sc05918e. eCollection 2023 Jan 25. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 36755706 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of ammosesters by mining the Streptomyces uncialis DCA2648 genome revealing new insight into ammosamide biosynthesis.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Jun 4;48(3-4):kuab027. doi: 10.1093/jimb/kuab027. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33982054 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Action of Ribosomally Synthesized and Post-Translationally Modified Peptides.Chem Rev. 2022 Sep 28;122(18):14722-14814. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00210. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Chem Rev. 2022. PMID: 36049139 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Guadêncio SP, MacMillan JB, Jensen PR, Fenical W. Ammosamides A and B New Cytotoxic Alkaloids Isolated from Marine Streptomyces sp. Planta Med. 2008;74:1083.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

