Osteopontin and integrin are involved in cholesterol gallstone formation
- PMID: 22207105
- PMCID: PMC3560682
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.882194
Osteopontin and integrin are involved in cholesterol gallstone formation
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate the role of osteopontin and its receptor, integrin αv, in gallstone formation using human tissue specimens and a guinea pig lithogenic model.
Material/methods: The nucleation role of osteopontin was determined in patients' and normal gallbladder bile samples in vitro. Normal gallbladder was the control, and gallstone gallbladders were divided into group I (with normal epithelia) and group II (with degenerated epithelia) based on pathology change. Immunostaining, mRNA and protein expressions of osteopontin and integrin αv were analyzed. The animals were randomly divided into a lithogenic diet group and a normal diet group; the osteopontin mRNA expression in gallbladder and liver and osteopontin concentrations were determined.
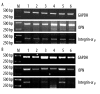
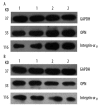
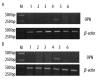
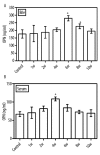
Results: Osteopontin prolonged nucleation time and inhibited the pro-nucleating role induced by calcium in human bile in vitro. Immunostaining for osteopontin and integrin αv in human gallbladder tissues showed a higher reactivity in Group I than control group and Group II. The immunostaining in Group II was weaker than control group; similar results were observed for mRNA and protein expression of osteopontin and integrin αv. In the animal assay, the mRNA expression and concentration of osteopontin in gallbladder and liver gradually increased at initial stages and decreased in later stages. The concentrations of osteopontin in bile and serum of guinea pig showed similar trends.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that osteopontin is involved in cholesterol gallstone formation, and the role of osteopontin might correlate with integrin αv and calcium.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Osteopontin Deficiency Alters Biliary Homeostasis and Protects against Gallstone Formation.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 3;6:30215. doi: 10.1038/srep30215. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27484115 Free PMC article.
-
Association of caveolin-3 and cholecystokinin A receptor with cholesterol gallstone disease in mice.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul 28;20(28):9513-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9513. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25071346 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin plays an anti-nucleation role in cholesterol gallstone formation.Hepatol Res. 2011 May;41(5):437-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2011.00790.x. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Hepatol Res. 2011. PMID: 21435127
-
Mucin genes in gallstone disease.Clin Chim Acta. 2012 Oct 9;413(19-20):1466-71. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2012.06.015. Epub 2012 Jun 13. Clin Chim Acta. 2012. PMID: 22705400 Review.
-
Hepatic cholesterol transport from plasma into bile: implications for gallstone disease.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2004 Jun;15(3):279-86. doi: 10.1097/00041433-200406000-00007. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2004. PMID: 15166783 Review.
Cited by
-
Osteopontin Deficiency Alters Biliary Homeostasis and Protects against Gallstone Formation.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 3;6:30215. doi: 10.1038/srep30215. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27484115 Free PMC article.
-
[New Progress in Longitudinal Research on the Risk Factors for Cholelithiasis].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Mar 20;55(2):490-500. doi: 10.12182/20240360508. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38645861 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Association between osteoporosis and gallstone based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2017-2020: a cross-sectional study.Front Public Health. 2025 Apr 8;13:1562984. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1562984. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40265049 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin Veto the Effects of Osteopontin (OPN) Specific Inhibitor on Leukemic Stem Cell Colony Forming Potential via Promotion of OPN Overexpression.Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2016 Jul 1;10(3):120-9. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2016. PMID: 27489587 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin (SPP1) expression on gallstone formation in rabbits fed with a lithogenic diet.J Adv Vet Anim Res. 2023 Jun 30;10(2):301-307. doi: 10.5455/javar.2023.j682. eCollection 2023 Jun. J Adv Vet Anim Res. 2023. PMID: 37534080 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaechele V, Wabitsch M, Thiere D, et al. Prevalence of gallbladder stone disease in obese children and adolescents: influence of the degree of obesity, sex, and pubertal development. J Pediat Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006;42:66. - PubMed
-
- Sipos P, Krisztina H, Blázovics A, Fehér J. Cholecystitis, gallstones and free radical reactions in human gallbladder. Med Sci Monit. 2001;7(1):84–88. - PubMed
-
- Shaffer EA. Gallstone disease: Epidemiology of gallbladder stone disease. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;20:981–96. - PubMed
-
- Yoo EH, Lee SY. The prevalence and risk factors for gallstone disease. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2009;47:795–807. - PubMed
-
- Everhart JE, Ruhl CE. Burden of digestive diseases in the United States Part III: Liver, biliary tract, and pancreas. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:1134–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

