Proton MR spectroscopy-detectable major neurotransmitters of the brain: biology and possible clinical applications
- PMID: 22207303
- PMCID: PMC4627491
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A2587
Proton MR spectroscopy-detectable major neurotransmitters of the brain: biology and possible clinical applications
Abstract
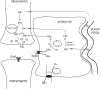
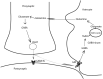
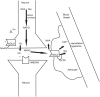
Neurotransmitters are chemical substances that, by definition, allow communication between neurons and permit most neuronal-glial interactions in the CNS. Approximately 80% of all neurons use glutamate, and almost all interneurons use GABA. A third neurotransmitter, NAAG, modulates glutamatergic neurotransmission. Concentration changes in these molecules due to defective synthetic machinery, receptor expression, or errors in their degradation and metabolism are accepted causes of several neurologic disorders. Knowledge of changes in neurotransmitter concentrations in the brain can add useful information in making a diagnosis, helping to pick the right drug of treatment, and monitoring patient response to drugs in a more objective manner. Recent advances in (1)H-MR spectroscopy hold promise in providing a more reliable in vivo detection of these neurotransmitters. In this article, we summarize the essential biology of 3 major neurotransmitters: glutamate, GABA, and NAAG. Finally we illustrate possible applications of (1)H-MR spectroscopy in neuroscience research.
Figures
References
-
- Braitenberg V, Schüz A. Cortex: Statistics and Geometry of Neuronal Connectivity. Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag; 1998
-
- Attwell D, Laughlin SB. An energy budget for signaling in the grey matter of the brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2001;21: 1133–45 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
