Functions of cholesterol and the cholesterol bilayer domain specific to the fiber-cell plasma membrane of the eye lens
- PMID: 22207480
- PMCID: PMC3288876
- DOI: 10.1007/s00232-011-9412-4
Functions of cholesterol and the cholesterol bilayer domain specific to the fiber-cell plasma membrane of the eye lens
Abstract
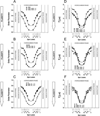
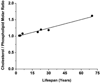
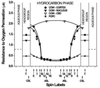
The most unique feature of the eye lens fiber-cell plasma membrane is its extremely high cholesterol content. Cholesterol saturates the bulk phospholipid bilayer and induces formation of immiscible cholesterol bilayer domains (CBDs) within the membrane. Our results (based on EPR spin-labeling experiments with lens-lipid membranes), along with a literature search, have allowed us to identify the significant functions of cholesterol specific to the fiber-cell plasma membrane, which are manifest through cholesterol-membrane interactions. The crucial role is played by the CBD. The presence of the CBD ensures that the surrounding phospholipid bilayer is saturated with cholesterol. The saturating cholesterol content in fiber-cell membranes keeps the bulk physical properties of lens-lipid membranes consistent and independent of changes in phospholipid composition. Thus, the CBD helps to maintain lens-membrane homeostasis when the membrane phospholipid composition changes significantly. The CBD raises the barrier for oxygen transport across the fiber-cell membrane, which should help to maintain a low oxygen concentration in the lens interior. It is hypothesized that the appearance of the CBD in the fiber-cell membrane is controlled by the phospholipid composition of the membrane. Saturation with cholesterol smoothes the phospholipid-bilayer surface, which should decrease light scattering and help to maintain lens transparency. Other functions of cholesterol include formation of hydrophobic and rigidity barriers across the bulk phospholipid-cholesterol domain and formation of hydrophobic channels in the central region of the membrane for transport of small, nonpolar molecules parallel to the membrane surface. In this review, we provide data supporting these hypotheses.
Figures







References
-
- Ashikawa I, Yin J-J, Subczynski WK, Kouyama T, Hyde JS, Kusumi A. Molecular organization and dynamics in bacteriorhodopsin-rich reconstituted membranes: discrimination of lipid environments by the oxygen transport parameter using a pulse ESR spin-labeling technique. Biochemistry. 1994;33:4947–4952. - PubMed
-
- Bach D, Wachtel E. Phospholipid/cholesterol model membranes: formation of cholesterol crystallites. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1610:187–197. - PubMed
-
- Barbazetto IA, Liang J, Chang S, Zheng L, Spector A, Dillon JP. Oxygen tension in the rabbit lens and vitreous before and after vitrectomy. Exp Eye Res. 2004;78:917–924. - PubMed
-
- Bassnett S, McNulty R. The effect of elevated intraocular oxygen on organelle degradation in the embryonic chicken lens. J Exp Biol. 2003;206:4353–4361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

