Structure and function of the small terminase component of the DNA packaging machine in T4-like bacteriophages
- PMID: 22207623
- PMCID: PMC3271864
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1110224109
Structure and function of the small terminase component of the DNA packaging machine in T4-like bacteriophages
Abstract
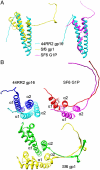
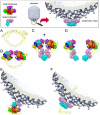
Tailed DNA bacteriophages assemble empty procapsids that are subsequently filled with the viral genome by means of a DNA packaging machine situated at a special fivefold vertex. The packaging machine consists of a "small terminase" and a "large terminase" component. One of the functions of the small terminase is to initiate packaging of the viral genome, whereas the large terminase is responsible for the ATP-powered translocation of DNA. The small terminase subunit has three domains, an N-terminal DNA-binding domain, a central oligomerization domain, and a C-terminal domain for interacting with the large terminase. Here we report structures of the central domain in two different oligomerization states for a small terminase from the T4 family of phages. In addition, we report biochemical studies that establish the function for each of the small terminase domains. On the basis of the structural and biochemical information, we propose a model for DNA packaging initiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
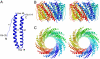

References
-
- Rao VB, Feiss M. The bacteriophage DNA packaging motor. Annu Rev Genet. 2008;42:647–681. - PubMed
-
- Smith DE, et al. The bacteriophage φ29 portal motor can package DNA against a large internal force. Nature. 2001;413:748–752. - PubMed
-
- Chemla YR, et al. Mechanism of force generation of a viral DNA packaging motor. Cell. 2005;122:683–692. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

