Positron emission tomography/computed tomography surveillance in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma in first remission has a low positive predictive value and high costs
- PMID: 22207683
- PMCID: PMC3366662
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2011.056010
Positron emission tomography/computed tomography surveillance in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma in first remission has a low positive predictive value and high costs
Abstract
Background: The value of performing post-therapy routine surveillance imaging in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma is controversial. This study evaluates the utility of positron emission tomography/computed tomography using 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxyglucose for this purpose and in situations with suspected lymphoma relapse.
Design and methods: We conducted a multicenter retrospective study. Patients with newly diagnosed Hodgkin lymphoma achieving at least a partial remission on first-line therapy were eligible if they received positron emission tomography/computed tomography surveillance during follow-up. Two types of imaging surveillance were analyzed: "routine" when patients showed no signs of relapse at referral to positron emission tomography/computed tomography, and "clinically indicated" when recurrence was suspected.
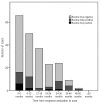
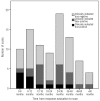
Results: A total of 211 routine and 88 clinically indicated positron emission tomography/computed tomography studies were performed in 161 patients. In ten of 22 patients with recurrence of Hodgkin lymphoma, routine imaging surveillance was the primary tool for the diagnosis of the relapse. Extranodal disease, interim positron emission tomography-positive lesions and positron emission tomography activity at response evaluation were all associated with a positron emission tomography/computed tomography-diagnosed preclinical relapse. The true positive rates of routine and clinically indicated imaging were 5% and 13%, respectively (P = 0.02). The overall positive predictive value and negative predictive value of positron emission tomography/computed tomography were 28% and 100%, respectively. The estimated cost per routine imaging diagnosed relapse was US$ 50,778.
Conclusions: Negative positron emission tomography/computed tomography reliably rules out a relapse. The high false positive rate is, however, an important limitation and a confirmatory biopsy is mandatory for the diagnosis of a relapse. With no proven survival benefit for patients with a pre-clinically diagnosed relapse, the high costs and low positive predictive value make positron emission tomography/computed tomography unsuitable for routine surveillance of patients with Hodgkin lymphoma.
Figures
Comment in
-
Positron emission tomography/computed tomography surveillance in patients with lymphoma: a fox hunt?Haematologica. 2012 Jun;97(6):797-9. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2012.063909. Haematologica. 2012. PMID: 22665528 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Engert A, Diehl V, Franklin J, Lohri A, Dörken B, Ludwig WD, et al. Escalated-dose BEACOPP in the treatment of patients with advanced-stage Hodgkin’s lymphoma: 10 years of follow-up of the GHSG HD9 study. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(27):4548–54. - PubMed
-
- Engert A, Plütschow A, Eich HT, Lohri A, Dörken B, Borchmann P, et al. Reduced treatment intensity in patients with early-stage Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(7):640–52. - PubMed
-
- Eich HT, Diehl V, Görgen H, Pabst T, Markova J, Debus J, et al. Intensified chemotherapy and dose-reduced involved-field radiotherapy in patients with early unfavorable Hodgkin’s lymphoma: final analysis of the German Hodgkin Study Group HD11 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(27):4199–206. - PubMed
-
- Lister TA, Crowther D, Sutcliffe SB, Glatstein E, Canellos GP, Young RC, et al. Report of a committee convened to discuss the evaluation and staging of patients with Hodgkin’s disease: Cotswolds meeting. J Clin Oncol. 1989;7(11):1630–6. - PubMed