Lexical and phonological effects in early word production
- PMID: 22207699
- PMCID: PMC3357200
- DOI: 10.1044/1092-4388(2011/10-0113)
Lexical and phonological effects in early word production
Abstract
Purpose: This study examines the influence of word frequency, phonological neighborhood density (PND), age of acquisition (AoA), and phonotactic probability on production variability and accuracy of known words by toddlers with no history of speech, hearing, or language disorders.
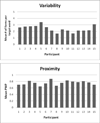
Method: Fifteen toddlers between 2;0 (years;months) and 2;5 produced monosyllabic target words varying in word frequency, PND, AoA, and phonotactic probability. Phonetic transcription was used to determine (a) whole-word variability and (b) proportion of whole-word proximity (PWP; Ingram, 2002) of each target word produced.
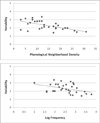
Results: Results show a significant effect of PND on PWP and variability (words from dense neighborhoods had higher PWP and lower variability than those from sparse neighborhoods), a significant effect of word frequency on variability (high-frequency words were less variable) but not proximity, and a significant effect of AoA on proximity (earlier acquired words had lower PWP) but not variability.
Conclusions: Results provide new information regarding the role that lexical and phonological factors play in the speech of young children; specifically, several factors are identified that influence variability of production. Additionally, by examining lexical and phonological factors simultaneously, the current study isolates differential effects of the individual factors. Implications for our understanding of emerging phonological representations are discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Aslin RN, Saffran JR, Newport EL. Computation of conditional probability statistics by 8-month-old infants. Psychological Science. 1998;9:321–324.
-
- Barry C, Johnston RA, Wood RF. Effects of age of acquisition, age, and repetition priming on object naming. Visual Cognition. 2006;13:911–927.
-
- Beckman ME, Edwards J. Lexical frequency effects on young children’s imitative productions. In: Broe MB, Pierrehumbert JB, editors. Papers in Laboratory Phonology: Vol. V. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2000. pp. 208–218.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources