Regulation of the ATP-sensitive potassium channel subunit, Kir6.2, by a Ca2+-dependent protein kinase C
- PMID: 22207763
- PMCID: PMC3307292
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.243923
Regulation of the ATP-sensitive potassium channel subunit, Kir6.2, by a Ca2+-dependent protein kinase C
Abstract
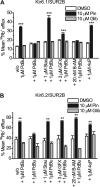
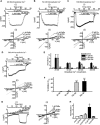
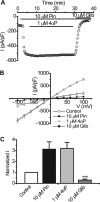
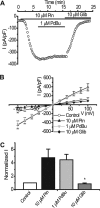
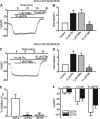
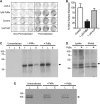
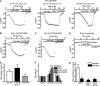
The activity of ATP-sensitive potassium (K(ATP)) channels is governed by the concentration of intracellular ATP and ADP and is thus responsive to the metabolic status of the cell. Phosphorylation of K(ATP) channels by protein kinase A (PKA) or protein kinase C (PKC) results in the modulation of channel activity and is particularly important in regulating smooth muscle tone. At the molecular level the smooth muscle channel is composed of a sulfonylurea subunit (SUR2B) and a pore-forming subunit Kir6.1 and/or Kir6.2. Previously, Kir6.1/SUR2B channels have been shown to be inhibited by PKC, and Kir6.2/SUR2B channels have been shown to be activated or have no response to PKC. In this study we have examined the modulation of channel complexes formed of the inward rectifier subunit, Kir6.2, and the sulfonylurea subunit, SUR2B. Using a combination of biochemical and electrophysiological techniques we show that this complex can be inhibited by protein kinase C in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner and that this inhibition is likely to be as a result of internalization. We identify a residue in the distal C terminus of Kir6.2 (Ser-372) whose phosphorylation leads to down-regulation of the channel complex. This inhibitory effect is distinct from activation which is seen with low levels of channel activity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A short motif in Kir6.1 consisting of four phosphorylation repeats underlies the vascular KATP channel inhibition by protein kinase C.J Biol Chem. 2008 Feb 1;283(5):2488-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M708769200. Epub 2007 Nov 29. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18048350 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase C modulation of recombinant ATP-sensitive K(+) channels composed of Kir6.1 and/or Kir6.2 expressed with SUR2B.J Physiol. 2002 May 15;541(Pt 1):65-80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.018101. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12015420 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in the mechanism of metabolic regulation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels containing Kir6.1 and Kir6.2 subunits.Cardiovasc Res. 2008 Sep 1;79(4):621-31. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn138. Epub 2008 Jun 3. Cardiovasc Res. 2008. PMID: 18522960
-
K(ATP) channel action in vascular tone regulation: from genetics to diseases.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2012 Feb 25;64(1):1-13. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 22348955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels by ADP and K+ channel openers: homology model of sulfonylurea receptor carboxyl-termini].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001 Sep;118(3):177-86. doi: 10.1254/fpj.118.177. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11577458 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Membrane potential and Ca2+ concentration dependence on pressure and vasoactive agents in arterial smooth muscle: A model.J Gen Physiol. 2015 Jul;146(1):79-96. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201511380. J Gen Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26123196 Free PMC article.
-
The role of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in cellular function and protection in the cardiovascular system.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Jan;171(1):12-23. doi: 10.1111/bph.12407. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24102106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Pharmacology of ATP-Sensitive K+ Channels (KATP).Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021;267:357-378. doi: 10.1007/164_2021_466. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34247283
-
Regulation of cardiac ATP-sensitive potassium channel surface expression by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 18;288(3):1568-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.429548. Epub 2012 Dec 6. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23223335 Free PMC article.
-
Subcellular trafficking and endocytic recycling of KATP channels.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 Jun 1;322(6):C1230-C1247. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00099.2022. Epub 2022 May 4. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35508187 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rodrigo G. C., Standen N. B. (2005) ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Curr. Pharm. Des. 11, 1915–1940 - PubMed
-
- Yellon D. M., Downey J. M. (2003) Preconditioning the myocardium: from cellular physiology to clinical cardiology. Physiol. Rev. 83, 1113–1151 - PubMed
-
- Babenko A. P., Aguilar-Bryan L., Bryan J. (1998) A view of SUR/Kir6.x, KATP channels. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 60, 667–687 - PubMed
-
- Seino S. (1999) ATP-sensitive potassium channels: a model of heteromultimeric potassium channel/receptor assemblies. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 61, 337–362 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

