The chemistry of peptidyltransferase center-targeted antibiotics: enzymatic resistance and approaches to countering resistance
- PMID: 22208312
- PMCID: PMC3499096
- DOI: 10.1021/cb200418f
The chemistry of peptidyltransferase center-targeted antibiotics: enzymatic resistance and approaches to countering resistance
Abstract
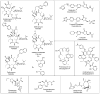
The continued ability to treat bacterial infections requires effective antibiotics. The development of new therapeutics is guided by knowledge of the mechanisms of action of and resistance to these antibiotics. Continued efforts to understand and counteract antibiotic resistance mechanisms at a molecular level have the potential to direct development of new therapeutic strategies in addition to providing insight into the underlying biochemical functions impacted by antibiotics. The interaction of antibiotics with the peptidyltransferase center and adjacent exit tunnel within the bacterial ribosome is the predominant mechanism by which antibiotics impede translation, thus stalling growth. Resistance enzymes catalyze the chemical modification of the RNA that composes these functional regions, leading to diminished binding of antibiotics. This review discusses recent advances in the elucidation of chemical mechanisms underlying resistance and driving the development of new antibiotics.
Figures



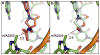
Similar articles
-
Resistance to linezolid caused by modifications at its binding site on the ribosome.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Feb;56(2):603-12. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05702-11. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22143525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
R chi-01, a new family of oxazolidinones that overcome ribosome-based linezolid resistance.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Oct;52(10):3550-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01193-07. Epub 2008 Jul 28. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18663023 Free PMC article.
-
The oxazolidinone antibiotics perturb the ribosomal peptidyl-transferase center and effect tRNA positioning.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 9;105(36):13339-44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804276105. Epub 2008 Aug 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18757750 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for context-specific inhibition of translation by oxazolidinone antibiotics.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2022 Feb;29(2):162-171. doi: 10.1038/s41594-022-00723-9. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35165456 Free PMC article.
-
[Ribosomal antibiotics].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2001 Jul-Aug;35(4):597-609. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2001. PMID: 11524946 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Capreomycin susceptibility is increased by TlyA-directed 2'-O-methylation on both ribosomal subunits.Mol Microbiol. 2012 Sep;85(6):1194-203. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08168.x. Epub 2012 Aug 1. Mol Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22779429 Free PMC article.
-
Three critical regions of the erythromycin resistance methyltransferase, ErmE, are required for function supporting a model for the interaction of Erm family enzymes with substrate rRNA.RNA. 2022 Feb;28(2):210-226. doi: 10.1261/rna.078946.121. Epub 2021 Nov 18. RNA. 2022. PMID: 34795028 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of cellular and molecular factors determining the response of cancer cells to six ergot alkaloids.Invest New Drugs. 2015 Feb;33(1):32-44. doi: 10.1007/s10637-014-0168-4. Epub 2014 Oct 25. Invest New Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25342140
-
Sequence specific detection of bacterial 23S ribosomal RNA by TLR13.Elife. 2012 Oct 30;1:e00102. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00102. Elife. 2012. PMID: 23110254 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic studies of the spore photoproduct lyase via a single cysteine mutation.Biochemistry. 2012 Sep 11;51(36):7173-88. doi: 10.1021/bi3010945. Epub 2012 Aug 31. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22906093 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wright GD. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Chem Commun. 2011;47:4055–4061. - PubMed
-
- Shlaes DM. Antibiotics: The perfect storm. Springer; New York: 2010. pp. 1–110.
-
- Walsh C. Antibiotics: Actions, origins, resistance. ASM Press; Washington, D.C.: 2003. pp. 1–340.
-
- Tenson T, Mankin A. Antibiotics and the ribosome. Mol Microbiol. 2006;59:1664–1677. - PubMed
-
- Wilson DN. The A-Z of bacterial translation inhibitors. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2009;44:393–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

