KMUP-1 inhibits L-type Ca²⁺ channels involved the protein kinase C in rat basilar artery myocytes
- PMID: 22208536
- PMCID: PMC11916799
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kjms.2011.10.026
KMUP-1 inhibits L-type Ca²⁺ channels involved the protein kinase C in rat basilar artery myocytes
Abstract
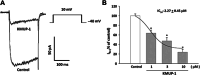
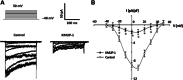
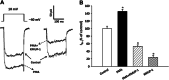
This study investigated whether KMUP-1, a xanthine-based derivative, inhibits L-type Ca(2+) currents (I(Ca,L)) in rat basilar artery smooth muscle cells (RBASMCs). We used whole cell patch-clamp recording to monitor Ba(2+) currents (I(Ba)) through L-type Ca(2+) channels (LTCCs). Under voltage-clamp conditions, holding at -40 mV, KMUP-1 (1, 3, 10 μM) inhibited I(Ba) in a concentration-dependent manner and its IC(50) value was 2.27 ± 0.45 μM. A high concentration of KMUP-1 (10 μM) showed without modifying the I(Ba) current-voltage relationship. On the other hand, the protein kinase C (PKC) activator phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA, 1 μM) increase I(Ba) was inhibited by KMUP-1. Pretreatment with the PKC inhibitor chelerythrine (5 μM) intensified KMUP-1-inhibited I(Ba). However, the Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 (30 μM) failed to affect the I(Ba) inhibition by KMUP-1. In light of these results, we suggest that KMUP-1 inhibition of LTCCs in concentration- and voltage-dependent manners in RBASMCs may be due, at least in part, to its modulation of the PKC pathway.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Taiwan LLC. All rights reserved.
Figures

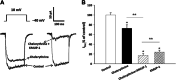
Similar articles
-
Restoration of uridine 5'-triphosphate-suppressed delayed rectifying K+ currents by an NO activator KMUP-1 involves RhoA/Rho kinase signaling in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2016 Dec;32(12):607-613. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2016.09.008. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27914611 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of voltage-gated L-type calcium channels by labedipinedilol-A involves protein kinase C in rat cerebrovascular smooth muscle cells.Vascul Pharmacol. 2009 Aug-Sep;51(2-3):65-71. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2009.03.001. Epub 2009 Mar 17. Vascul Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19298869
-
KMUP-1 activates BKCa channels in basilar artery myocytes via cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases.Br J Pharmacol. 2005 Nov;146(6):862-71. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706387. Br J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16151435 Free PMC article.
-
The Xanthine Derivative KMUP-1 Attenuates Serotonin-Induced Vasoconstriction and K⁺-Channel Inhibitory Activity via the PKC Pathway in Pulmonary Arteries.Int J Biol Sci. 2015 Apr 25;11(6):633-42. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.11127. eCollection 2015. Int J Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25999786 Free PMC article.
-
KMUP-1 inhibits pulmonary artery proliferation by targeting serotonin receptors/transporter and NO synthase, inactivating RhoA and suppressing AKT/ERK phosphorylation.Vascul Pharmacol. 2010 Nov-Dec;53(5-6):239-49. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2010.09.003. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Vascul Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20870034
Cited by
-
Actions of KMUP-1, a xanthine and piperazine derivative, on voltage-gated Na(+) and Ca(2+) -activated K(+) currents in GH3 pituitary tumour cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Nov;172(21):5110-22. doi: 10.1111/bph.13276. Epub 2015 Oct 25. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26276211 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of uridine 5'-triphosphate-suppressed delayed rectifying K+ currents by an NO activator KMUP-1 involves RhoA/Rho kinase signaling in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2016 Dec;32(12):607-613. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2016.09.008. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27914611 Free PMC article.
-
BKCa Channel Inhibition by Peripheral Nerve Injury Is Restored by the Xanthine Derivative KMUP-1 in Dorsal Root Ganglia.Cells. 2021 Apr 20;10(4):949. doi: 10.3390/cells10040949. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33923953 Free PMC article.
-
A xanthine-derivative K(+)-channel opener protects against serotonin-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy via the modulation of protein kinases.Int J Biol Sci. 2013 Dec 17;10(1):64-72. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.7894. eCollection 2013. Int J Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24391452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Slish D.F., Welsh D.G., Brayden J.E.. Diacylglycerol and protein kinase C activate cation channels involved in myogenic tone. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002; 283: H2196–H2201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

