Genesis of a novel Shigella flexneri serotype by sequential infection of serotype-converting bacteriophages SfX and SfI
- PMID: 22208551
- PMCID: PMC3306764
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-269
Genesis of a novel Shigella flexneri serotype by sequential infection of serotype-converting bacteriophages SfX and SfI
Abstract
Background: Shigella flexneri is the major pathogen causing bacillary dysentery. Fifteen serotypes have been recognized up to now. The genesis of new S. flexneri serotypes is commonly mediated by serotype-converting bacteriophages. Untypeable or novel serotypes from natural infections had been reported worldwide but have not been generated in laboratory.
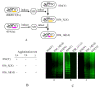
Results: A new S. flexneri serotype-serotype 1 d was generated when a S. flexneri serotype Y strain (native LPS) was sequentially infected with 2 serotype-converting bacteriophages, SfX first and then SfI. The new serotype 1 d strain agglutinated with both serotype X-specific anti-7;8 grouping serum and serotype 1a-specific anti- I typing serum, and differed from subserotypes 1a, 1b and 1c. Twenty four S. flexneri clinical isolates of serotype X were all converted to serotype 1 d by infection with phage SfI. PCR and sequencing revealed that SfI and SfX were integrated in tandem into the proA-yaiC region of the host chromosome.
Conclusions: These findings suggest a new S. flexneri serotype could be created in nature. Such a conversion may be constrained by susceptibility of a strain to infection by a given serotype-converting bacteriophage. This finding has significant implications in the emergence of new S. flexneri serotypes in nature.
Figures
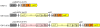
References
-
- Clemens JD, Kotloff KL, Kay B. Generic protocol to estimate the burden o Shigell diarrhoea and dysenteric mortalit. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1999.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

