Reduced expression of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 contributes to apoptosis and angiogenesis in cervical cancer
- PMID: 22208663
- PMCID: PMC3314549
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-31-1
Reduced expression of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 contributes to apoptosis and angiogenesis in cervical cancer
Abstract
Background: Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 (TFPI-2) is an extracellular matrix associated broad-spectrum Kunitz-type serine proteinase inhibitor. Recently, down regulation of TFPI-2 was suggested to be involved in tumor invasion and metastasis in some cancers.
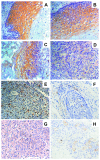
Methods: This study involved 12 normal cervical squamous epithelia, 48 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), and 68 cervical cancer. The expression of TFPI-2, Ki-67 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were investigated by immunohistochemistry staining. The apoptolic index(AI) was determined with an in situ end-labeling assay(TUNEL). And the marker of CD34 staining was used as an indicator of microvessel density (MVD).
Results: TFPI-2 expression has a decreasing trend with the progression of cervical cancer and was significantly correlated with FIGO stage, lymph node metastasis and HPV infection. In addition, there were significant positive correlations between the grading of TFPI-2 expression and AI(P=0.004). In contrast, the expression of TFPI-2 and VEGF or MVD was negatively correlated (both p < 0.001). However, we did not establish any significant correlation between Ki-67 and TFPI-2 expression in cervical cancer.
Conclusions: The results suggested that the expression of TFPI-2 had a decreasing trend with tumor progression of cervical cancer. There was a close association between the expression of TFPI-2 and tumor cell apoptosis and angiogenesis in patients with cervical cancer. TFPI-2 may play an inhibitive role during the development of cervical cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Angiogenesis is associated with vascular endothelial growth factor expression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia.Br J Cancer. 1997;76(11):1410-5. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1997.571. Br J Cancer. 1997. PMID: 9400935 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of VEGF, c-fms and COX-2 expression correlates with severity of cervical cancer precursor (CIN) lesions and invasive disease.Gynecol Oncol. 2008 Sep;110(3):445-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.04.038. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Gynecol Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18565574
-
Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in the progression of cervical neoplasia and its relation to angiogenesis and p53 status.Anal Quant Cytol Histol. 2003 Dec;25(6):303-11. Anal Quant Cytol Histol. 2003. PMID: 14714296
-
[Remodeling of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in cervical cancer development].Biomed Khim. 2015 Sep-Oct;61(5):579-97. doi: 10.18097/PBMC20156105579. Biomed Khim. 2015. PMID: 26539865 Review. Russian.
-
The role of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 in cancer biology.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2007 Oct;33(7):653-9. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-991532. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2007. PMID: 18000791 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effects of ascorbic acid against anticancer drug-induced oxidative stress and genotoxic damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.3 Biotech. 2025 May;15(5):118. doi: 10.1007/s13205-025-04280-y. Epub 2025 Apr 7. 3 Biotech. 2025. PMID: 40206055
-
Re-expression of Selected Epigenetically Silenced Candidate Tumor Suppressor Genes in Cervical Cancer by TET2-directed Demethylation.Mol Ther. 2016 Mar;24(3):536-47. doi: 10.1038/mt.2015.226. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Mol Ther. 2016. PMID: 26686387 Free PMC article.
-
The role of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 in malignant transformation of sinonasal inverted papilloma.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014 Aug;271(8):2191-6. doi: 10.1007/s00405-013-2840-2. Epub 2013 Dec 7. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014. PMID: 24318421
-
Methylation-induced downregulation of TFPI-2 causes TMPRSS4 overexpression and contributes to oncogenesis in a subset of non-small-cell lung carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2015 Jan;106(1):34-42. doi: 10.1111/cas.12569. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 25414083 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Trials of Antiangiogenesis Therapy in Recurrent/Persistent and Metastatic Cervical Cancer.Oncologist. 2016 May;21(5):576-85. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0393. Epub 2016 Mar 29. Oncologist. 2016. PMID: 27026677 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moscicki AB, Schiffman M, Kjaer S, Villa LL. Chapter 5: updating the natural history of HPV and anogenital cancer. Vaccine. 2006;24(suppl 3):S42–51. - PubMed
-
- Udagawa K, Yasumitsu H, Esaki M, Sawada H, Nagashima Y, Aoki I, Jin M, Miyagi E, Nakazawa T, Hirahara F, Miyazaki K, Miyagi Y. Subcellularlocalization of PP5/TFPI-2 in human placenta: a possible role of PP5/TFPI-2 as an anti-coagulantonthe surface of syncytiotrophoblasts. Placenta. 2002;23:145–153. doi: 10.1053/plac.2001.0774. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sugiyama T, Ishii S, Yamamoto J, Irie R, Saito K, Otuki T, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, Hio Y, Ota T, Nishikawa T, Sugano S, Masuho Y, Isogai T. cDNA macroarray analysis of gene expression in synoviocytes stimulated with TNF alpha. FEBS Lett. 2002;517:121–128. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(02)02588-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

