Disturbances of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and plasma electrolytes during experimental sepsis
- PMID: 22208725
- PMCID: PMC3264499
- DOI: 10.1186/2110-5820-1-53
Disturbances of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and plasma electrolytes during experimental sepsis
Abstract
Background: Sepsis continues to be a poorly understood syndrome with a high mortality rate. While we are beginning to decipher the intricate interplay of the inflammatory response during sepsis, the precise regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and its impact on electrolyte homeostasis during sepsis remains incompletely understood.
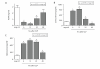
Methods: Sepsis was induced in adult male Sprague-Dawley rats by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). Plasma samples were obtained as a function of time (6-48 hrs) after CLP and compared with healthy animals (neg ctrl). Samples were analyzed for adrenocorticotropin (ACTH), corticosterone, and aldosterone levels, as well as concentrations of sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), chloride (Cl-), and magnesium (Mg2+).
Results: ACTH levels were found to be significantly reduced 6-24 hrs after CLP in comparison to baseline levels and displayed gradual recovery during the later course (24-48 hrs) of sepsis. Plasma corticosterone concentrations exhibited a bell-shaped response, peaking between 6 and 12 hrs followed by rapid decline and concentrations below negative control levels 48 hrs after injury. Aldosterone levels in septic animals were continuously elevated between 6 and 48 hrs. Whereas plasma Na+ levels were found to be persistently elevated following CLP, levels of K+, Cl- and Mg2+ were significantly reduced as a function of time and gradually recovered during the later course of sepsis.
Conclusions: CLP-induced sepsis resulted in dynamic changes of ACTH, corticosterone, and aldosterone levels. In addition, electrolyte levels showed significant disturbances after CLP. These electrolyte perturbations might be evoked by a downstream effect or a dysfunctional HPA-axis response during sepsis and contribute to severe complications during sepsis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adrenal insufficiency during the late stage of polymicrobial sepsis.Crit Care Med. 2001 Mar;29(3):618-22. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200103000-00026. Crit Care Med. 2001. PMID: 11373430
-
Cecal ligation and puncture in rats interrupts the circadian rhythms of corticosterone and adrenocortical responsiveness to adrenocorticotrophic hormone.Crit Care Med. 2006 Apr;34(4):1178-84. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000207340.24290.3C. Crit Care Med. 2006. PMID: 16484905
-
Intrahepatic nuclear factor-kappa B activity and alpha 1-acid glycoprotein transcription do not predict outcome after cecal ligation and puncture in the rat.Crit Care Med. 2001 Mar;29(3):589-96. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200103000-00021. Crit Care Med. 2001. PMID: 11373425
-
Delayed administration of human inter-alpha inhibitor proteins reduces mortality in sepsis.Crit Care Med. 2004 Aug;32(8):1747-52. doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000132903.14121.0e. Crit Care Med. 2004. PMID: 15286553
-
[The relationship of ultrastructure and function of hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis in early stage of sepsis in rats].Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2011 May;23(5):286-9. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2011. PMID: 21549066 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Sepsis-associated encephalopathy: a vicious cycle of immunosuppression.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Jan 10;17(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-1701-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 31924221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Where there is sodium there may be sepsis.J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2019 Sep 5;9(4):296-299. doi: 10.1080/20009666.2019.1634407. eCollection 2019. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2019. PMID: 31528275 Free PMC article.
-
Vasopressin Impairment During Sepsis Is Associated with Hypothalamic Intrinsic Apoptotic Pathway and Microglial Activation.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Sep;54(7):5526-5533. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0094-x. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27631877
-
Dynamic Intracranial Pressure Waveform Morphology Predicts Ventriculitis.Neurocrit Care. 2022 Apr;36(2):404-411. doi: 10.1007/s12028-021-01303-3. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Neurocrit Care. 2022. PMID: 34331206 Free PMC article.
-
Immunity's fourth dimension: approaching the circadian-immune connection.Trends Immunol. 2012 Dec;33(12):607-12. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2012.08.007. Epub 2012 Sep 20. Trends Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23000010 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kung HC, Hoyert DL, Xu J, Murphy SL. Deaths: final data for 2005. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2008;56(10):1–120. - PubMed
-
- Annane D, Vignon P, Renault A, Bollaert PE, Charpentier C, Martin C, Troche G, Ricard JD, Nitenberg G, Papazian L. et al.Norepinephrine plus dobutamine versus epinephrine alone for management of septic shock: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2007;370(9588):676–684. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61344-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zeiher BG, Steingrub J, Laterre PF, Dmitrienko A, Fukiishi Y, Abraham E. LY315920NA/S-5920, a selective inhibitor of group IIA secretory phospholipase A2, fails to improve clinical outcome for patients with severe sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2005;33(8):1741–1748. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000171540.54520.69. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

