COL4A2 mutations impair COL4A1 and COL4A2 secretion and cause hemorrhagic stroke
- PMID: 22209247
- PMCID: PMC3257894
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.11.022
COL4A2 mutations impair COL4A1 and COL4A2 secretion and cause hemorrhagic stroke
Abstract
Collagen, type IV, alpha 1 (COL4A1) and alpha 2 (COL4A2) form heterotrimers and are abundant components of basement membranes, including those of the cerebral vasculature. COL4A1 mutations are an increasingly recognized cause of multisystem disorders, including highly penetrant cerebrovascular disease and intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). Because COL4A1 and COL4A2 are structurally and functionally associated, we hypothesized that variants in COL4A2 would also cause ICH. We sequence COL4A2 in 96 patients with ICH and identify three rare, nonsynonymous coding variants in four patients that are not present in a cohort of 144 ICH-free individuals. All three variants change evolutionarily conserved amino acids. Using a cellular assay, we show that these putative mutations cause intracellular accumulation of COL4A1 and COL4A2 at the expense of their secretion, which supports their pathogenecity. Furthermore, we show that Col4a2 mutant mice also have completely penetrant ICH and that mutations in mouse and human lead to retention of COL4A1 and COL4A2 within the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Importantly, two of the three putative mutations found in patients trigger ER stress and activate the unfolded protein response. The identification of putative COL4A2 mutations that might contribute to ICH in human patients provides insight into the pathogenic mechanisms of this disease. Our data suggest that COL4A2 mutations impair COL4A1 and COL4A2 secretion and can also result in cytotoxicity. Finally, our findings suggest that, collectively, mutations in COL4A1 and COL4A2 contribute to sporadic cases of ICH.
Copyright © 2012 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


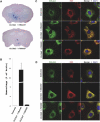

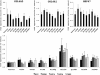
References
-
- Qureshi A.I., Tuhrim S., Broderick J.P., Batjer H.H., Hondo H., Hanley D.F. Spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001;344:1450–1460. - PubMed
-
- Rosand J., Eckman M.H., Knudsen K.A., Singer D.E., Greenberg S.M. The effect of warfarin and intensity of anticoagulation on outcome of intracerebral hemorrhage. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004;164:880–884. - PubMed
-
- Gould D.B., Phalan F.C., van Mil S.E., Sundberg J.P., Vahedi K., Massin P., Bousser M.G., Heutink P., Miner J.H., Tournier-Lasserve E., John S.W. Role of COL4A1 in small-vessel disease and hemorrhagic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006;354:1489–1496. - PubMed
-
- Gould D.B., Phalan F.C., Breedveld G.J., van Mil S.E., Smith R.S., Schimenti J.C., Aguglia U., van der Knaap M.S., Heutink P., John S.W.M. Mutations in Col4a1 cause perinatal cerebral hemorrhage and porencephaly. Science. 2005;308:1167–1171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

