Mad2 and Mad3 cooperate to arrest budding yeast in mitosis
- PMID: 22209528
- PMCID: PMC3277655
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.12.029
Mad2 and Mad3 cooperate to arrest budding yeast in mitosis
Abstract
Background: The spindle checkpoint ensures accurate chromosome transmission by delaying chromosome segregation until all chromosomes are correctly aligned on the mitotic spindle. The checkpoint is activated by kinetochores that are not attached to microtubules or are attached but not under tension and arrests cells at metaphase by inhibiting the anaphase-promoting complex (APC) and its coactivator Cdc20. Despite numerous studies, we still do not understand how the checkpoint proteins coordinate with each other to inhibit APC(Cdc20) activity.
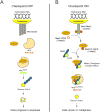
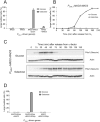
Results: To ask how the checkpoint components induce metaphase arrest, we constructed fusions of checkpoint proteins and expressed them in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae to mimic possible protein interactions during checkpoint activation. We found that expression of a Mad2-Mad3 protein fusion or noncovalently linked Mad2 and Mad3, but not the overexpression of the two separate proteins, induces metaphase arrest that is independent of functional kinetochores or other checkpoint proteins. We further showed that artificially tethering Mad2 to Cdc20 also arrests cells in metaphase independently of other checkpoint components.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that Mad3 is required for the stable binding of Mad2 to Cdc20 in vivo, which is sufficient to inhibit APC activity and is the most downstream event in spindle checkpoint activation.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
Mitosis: short-circuiting spindle checkpoint signaling.Curr Biol. 2012 Feb 21;22(4):R128-30. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.01.018. Curr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22361149
References
-
- Li R, Murray AW. Feedback control of mitosis in budding yeast. Cell. 1991;66:519–531. - PubMed
-
- Hoyt MA, Totis L, Roberts BT. S. cerevisiae genes required for cell cycle arrest in response to loss of microtubule function. Cell. 1991;66:507–517. - PubMed
-
- Li X, Nicklas RB. Mitotic forces control a cell-cycle checkpoint. Nature. 1995;373:630–632. - PubMed
-
- Stern BM, Murray AW. Lack of tension at kinetochores activates the spindle checkpoint in budding yeast. Curr Biol. 2001;11:1462–1467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

