Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) is an essential modifier of glucocorticoid-induced hepatic gluconeogenesis
- PMID: 22210316
- PMCID: PMC3266407
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-0313
Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) is an essential modifier of glucocorticoid-induced hepatic gluconeogenesis
Abstract
In the current study, we investigated the importance of histone deacetylase (HDAC)6 for glucocorticoid receptor-mediated effects on glucose metabolism and its potential as a therapeutic target for the prevention of glucocorticoid-induced diabetes. Dexamethasone-induced hepatic glucose output and glucocorticoid receptor translocation were analyzed in wild-type (wt) and HDAC6-deficient (HDAC6KO) mice. The effect of the specific HDAC6 inhibitor tubacin was analyzed in vitro. wt and HDAC6KO mice were subjected to 3 weeks' dexamethasone treatment before analysis of glucose and insulin tolerance. HDAC6KO mice showed impaired dexamethasone-induced hepatic glucocorticoid receptor translocation. Accordingly, dexamethasone-induced expression of a large number of hepatic genes was significantly attenuated in mice lacking HDAC6 and by tubacin in vitro. Glucose output of primary hepatocytes from HDAC6KO mice was diminished. A significant improvement of dexamethasone-induced whole-body glucose intolerance as well as insulin resistance in HDAC6KO mice compared with wt littermates was observed. This study demonstrates that HDAC6 is an essential regulator of hepatic glucocorticoid-stimulated gluconeogenesis and impairment of whole-body glucose metabolism through modification of glucocorticoid receptor nuclear translocation. Selective pharmacological inhibition of HDAC6 may provide a future therapeutic option against the prodiabetogenic actions of glucocorticoids.
Figures

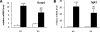
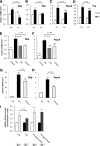
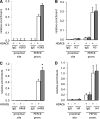
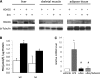
Comment in
-
Comment on: Winkler et al. Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) is an essential modifier of glucocorticoid-induced hepatic gluconeogenesis. Diabetes 2012;61:513-523.Diabetes. 2012 Jul;61(7):e10; author reply e11. doi: 10.2337/db12-0323. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22723278 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Trikudanathan S, McMahon GT. Optimum management of glucocorticoid-treated patients. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2008;4:262–271 - PubMed
-
- Andrews RC, Walker BR. Glucocorticoids and insulin resistance: old hormones, new targets. Clin Sci (Lond) 1999;96:513–523 - PubMed
-
- Arner P, Gunnarsson R, Blomdahl S, Groth CG. Some characteristics of steroid diabetes: a study in renal-transplant recipients receiving high-dose corticosteroid therapy. Diabetes Care 1983;6:23–25 - PubMed
-
- Bernal-Mizrachi C, Weng S, Feng C, et al. Dexamethasone induction of hypertension and diabetes is PPAR-alpha dependent in LDL receptor-null mice. Nat Med 2003;9:1069–1075 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

