Glucocorticoid signaling in the arcuate nucleus modulates hepatic insulin sensitivity
- PMID: 22210324
- PMCID: PMC3266416
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-1239
Glucocorticoid signaling in the arcuate nucleus modulates hepatic insulin sensitivity
Abstract
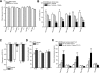
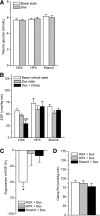
Glucocorticoid receptors are highly expressed in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and arcuate nucleus (ARC). As glucocorticoids have pronounced effects on neuropeptide Y (NPY) expression and as NPY neurons projecting from the ARC to the PVN are pivotal for balancing feeding behavior and glucose metabolism, we investigated the effect of glucocorticoid signaling in these areas on endogenous glucose production (EGP) and insulin sensitivity by local retrodialysis of the glucocorticoid receptor agonist dexamethasone into the ARC or the PVN, in combination with isotope dilution and hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp techniques. Retrodialysis of dexamethasone for 90 min into the ARC or the PVN did not have significant effects on basal plasma glucose concentration. During the hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp, retrodialysis of dexamethasone into the ARC largely prevented the suppressive effect of hyperinsulinemia on EGP. Antagonizing the NPY1 receptors by intracerebroventricular infusion of its antagonist largely blocked the hepatic insulin resistance induced by dexamethasone in the ARC. The dexamethasone-ARC-induced inhibition of hepatic insulin sensitivity was also prevented by hepatic sympathetic denervation. These data suggest that glucocorticoid signaling specifically in the ARC neurons modulates hepatic insulin responsiveness via NPY and the sympathetic system, which may add to our understanding of the metabolic impact of clinical conditions associated with hypercortisolism.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intracerebroventricular administration of neuropeptide Y induces hepatic insulin resistance via sympathetic innervation.Diabetes. 2008 Sep;57(9):2304-10. doi: 10.2337/db07-1658. Epub 2008 Jun 10. Diabetes. 2008. PMID: 18544708 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in the sympathoexcitatory response to insulin in obese rats: role of neuropeptide Y.J Physiol. 2019 Mar;597(6):1757-1775. doi: 10.1113/JP277517. Epub 2019 Feb 3. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30628058 Free PMC article.
-
A major role for perifornical orexin neurons in the control of glucose metabolism in rats.Diabetes. 2009 Sep;58(9):1998-2005. doi: 10.2337/db09-0385. Epub 2009 Jul 10. Diabetes. 2009. PMID: 19592616 Free PMC article.
-
Growth hormone inhibits its own secretion by acting on the hypothalamus through its receptors on neuropeptide Y neurons in the arcuate nucleus and somatostatin neurons in the periventricular nucleus.Endocr J. 1998 Apr;45 Suppl:S19-26. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.45.suppl_s19. Endocr J. 1998. PMID: 9790225 Review.
-
Neuropeptide Y, the hypothalamus, and diabetes: insights into the central control of metabolism.Peptides. 1995;16(4):757-71. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(94)00200-p. Peptides. 1995. PMID: 7479313 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance: focus on adipose tissue function and lipid metabolism.Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2014 Mar;43(1):75-102. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2013.10.005. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2014. PMID: 24582093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Abnormalities of Chronic High-Dose Glucocorticoids Are Not Mediated by Hypothalamic AgRP in Male Mice.Endocrinology. 2019 May 1;160(5):964-978. doi: 10.1210/en.2019-00018. Endocrinology. 2019. PMID: 30794724 Free PMC article.
-
Lifestyle interventions for the prevention and treatment of hypertension.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021 Apr;18(4):251-275. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-00437-9. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33037326 Review.
-
Zinc Finger Transcription Factor Zbtb16 Coordinates the Response to Energy Deficit in the Mouse Hypothalamus.Front Neurosci. 2020 Dec 1;14:592947. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.592947. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33335471 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothalamic innate immune reaction in obesity.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015 Jun;11(6):339-51. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2015.48. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25824676 Review.
References
-
- Reinartz G, Angermaier A, Buchfelder M, Fahlbusch R, Georgieff M. Pre- and postoperative investigations of hepatic glucose production and leucine turnover in Cushing’s disease utilizing stable isotope techniques. Horm Metab Res 1995;27:425–431 - PubMed
-
- Obici S, Zhang BB, Karkanias G, Rossetti L. Hypothalamic insulin signaling is required for inhibition of glucose production. Nat Med 2002;8:1376–1382 - PubMed
-
- Könner AC, Janoschek R, Plum L, et al. Insulin action in AgRP-expressing neurons is required for suppression of hepatic glucose production. Cell Metab 2007;5:438–449 - PubMed
-
- Klieverik LP, Sauerwein HP, Ackermans MT, Boelen A, Kalsbeek A, Fliers E. Effects of thyrotoxicosis and selective hepatic autonomic denervation on hepatic glucose metabolism in rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2008;294:E513–E520 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

