Efficacy and safety of exenatide once weekly versus metformin, pioglitazone, and sitagliptin used as monotherapy in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes (DURATION-4): a 26-week double-blind study
- PMID: 22210563
- PMCID: PMC3263915
- DOI: 10.2337/dc11-1107
Efficacy and safety of exenatide once weekly versus metformin, pioglitazone, and sitagliptin used as monotherapy in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes (DURATION-4): a 26-week double-blind study
Abstract
Objective: To test the safety and efficacy of exenatide once weekly (EQW) compared with metformin (MET), pioglitazone (PIO), and sitagliptin (SITA) over 26 weeks, in suboptimally treated (diet and exercise) drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes.
Research design and methods: Patients were randomized to subcutaneous (SC) EQW 2.0 mg + oral placebo (n = 248), MET 2,000 mg/day + SC placebo (n = 246), PIO 45 mg/day + SC placebo (n = 163), or SITA 100 mg/day + SC placebo (n = 163) for 26 weeks. MET and PIO therapies were increased to maximum-tolerated dosages. Injections with EQW or placebo were administered weekly, while oral medication or placebo was administered daily.
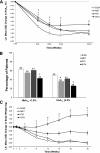
Results: Baseline characteristics were as follows: 59% men, 67% Caucasian, mean age 54 years, HbA(1c) 8.5%, fasting serum glucose 9.9 mmol/L, body weight 87.0 kg, and diabetes duration 2.7 years. HbA(1c) reductions (%) at 26 weeks (least-squares means) with EQW versus MET, PIO, and SITA were -1.53 vs. -1.48 (P = 0.620), -1.63 (P = 0.328), and -1.15 (P < 0.001), respectively. Weight changes (kg) were -2.0 vs. -2.0 (P = 0.892), +1.5 (P < 0.001), and -0.8 (P < 0.001), respectively. Common adverse events were as follows: EQW, nausea (11.3%) and diarrhea (10.9%); MET, diarrhea (12.6%) and headache (12.2%); PIO, nasopharyngitis (8.6%) and headache (8.0%); and SIT, nasopharyngitis (9.8%) and headache (9.2%). Minor (confirmed) hypoglycemia was rarely reported. No major hypoglycemia occurred.
Conclusions: EQW was noninferior to MET but not PIO and superior to SITA with regard to HbA(1c) reduction at 26 weeks. Of the agents studied, EQW and MET provided similar improvements in glycemic control along with the benefit of weight reduction and no increased risk of hypoglycemia.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00676338.
Figures

References
-
- Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, et al. Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009;32:193–20310.2337/dc08-9025 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schernthaner G, Matthews DR, Charbonnel B, Hanefeld M, Brunetti P; Quartet [corrected] Study Group Efficacy and safety of pioglitazone versus metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a double-blind, randomized trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004;89:6068–607610.1210/jc.2003-030861 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moretto TJ, Milton DR, Ridge TD, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of exenatide monotherapy over 24 weeks in antidiabetic drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Clin Ther 2008;30:1448–146010.1016/j.clinthera.2008.08.006 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

