P-wave dispersion for predicting paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in acute ischemic stroke
- PMID: 22211098
- PMCID: PMC3245420
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.9.108
P-wave dispersion for predicting paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in acute ischemic stroke
Abstract
Background: Detection of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (PAF) in acute ischemic stroke patients poses diagnostic challenge. The aim of this study was to predict the presence of PAF by means of 12-lead ECG in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Our hypothesis was that P-wave dispersion (P(d)) might be a useful marker in predicting PAF in patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Methods: 12-lead resting ECGs, 24-hour Holter recordings and echocardiograms of 400 patients were analyzed retrospectively. PAF was detected in 40 patients on 24-hour Holter monitoring. Forty out of 360 age and gender matched patients without PAF were randomly chosen and assigned as the control group. Demographics, P-wave characteristics and echocardiographic findings of the patients with and without PAF were compared.
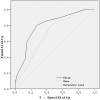
Results: Maximum P-wave duration (p=0.002), P(d) (p<0.001) and left atrium diameter (p=0.04) were significantly higher in patients with PAF when compared to patients without PAF. However, in binary logistic regression analysis P(d) was the only independent predictor of PAF. The cut-off value of P(d) for the detection of PAF was 57.5 milliseconds (msc). Area under the curve was 0.80 (p<0.001). On a single 12-lead ECG, a value higher than 57.5 msc predicted the presence of PAF with a sensitivity of 80% and a specificity of 73%.
Conclusion: P(d) on a single 12-lead ECG obtained within 24 hours of an acute ischemic stroke might help to predict PAF and reduce the risk of recurrent strokes.
Keywords: 12-lead ECG; 24- hour Holter monitoring.; P-wave dispersion; acute ischemic stroke; paroxysmal atrial fibrillation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Camm AJ, Kirchhof P, Lip GY. et al. Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: the Task Force for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur Heart J. 2010;31:2369–429. - PubMed
-
- Adams HP Jr, del Zoppo G, Alberts MJ. et al. Guidelines for the early management of adults with ischemic stroke: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council, Clinical Cardiology Council, Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention Council, and the Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease and Quality of Care Outcomes in Research Interdisciplinary Working Groups: the American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline as an educational tool for neurologists. Stroke. 2007;38:1655–711. - PubMed
-
- Liao J, Khalid Z, Scallan C, Morillo C, O'Donnell M. Noninvasive cardiac monitoring for detecting paroxysmal atrial fibrillation or flutter after acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review. Stroke. 2007;38:2935–40. - PubMed
-
- Fujii S, Shibazaki K, Iguchi Y, Sakai K, Kimura K. [Relationship between left atrial size and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in acute ischemic stroke] Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2009;49:629–33. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

