Immune-related microRNAs are abundant in breast milk exosomes
- PMID: 22211110
- PMCID: PMC3248653
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.8.118
Immune-related microRNAs are abundant in breast milk exosomes
Abstract
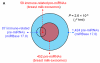
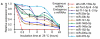
Breast milk is a complex liquid rich in immunological components that affect the development of the infant's immune system. Exosomes are membranous vesicles of endocytic origin that are found in various body fluids and that can mediate intercellular communication. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a well-defined group of non-coding small RNAs, are packaged inside exosomes in human breast milk. Here, we identified 602 unique miRNAs originating from 452 miRNA precursors (pre-miRNAs) in human breast milk exosomes using deep sequencing technology. We found that, out of 87 well-characterized immune-related pre-miRNAs, 59 (67.82%) are presented and enriched in breast milk exosomes (P < 10(-16), χ(2) test). In addition, compared with exogenous synthetic miRNAs, these endogenous immune-related miRNAs are more resistant to relatively harsh conditions. It is, therefore, tempting to speculate that these exosomal miRNAs are transferred from the mother's milk to the infant via the digestive tract, and that they play a critical role in the development of the infant immune system.
Keywords: breast milk; deep sequencing.; exosome; immune-related miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
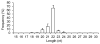







References
-
- Admyre C, Johansson SM, Qazi KR, Filen JJ, Lahesmaa R. et al. Exosomes with immune modulatory features are present in human breast milk. J Immunol. 2007;179:1969–1978. - PubMed
-
- Petherick A. Development: mother's milk: a rich opportunity. Nature. 2010;468:S5–7. - PubMed
-
- Théry C, Ostrowski M, Segura E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:581–593. - PubMed
-
- Mathivanan S, Ji H, Simpson RJ. Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J Proteomics. 2010;73:1907–1920. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

