The olfactory co-receptor Orco from the migratory locust (Locusta migratoria) and the desert locust (Schistocerca gregaria): identification and expression pattern
- PMID: 22211114
- PMCID: PMC3248701
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.8.159
The olfactory co-receptor Orco from the migratory locust (Locusta migratoria) and the desert locust (Schistocerca gregaria): identification and expression pattern
Abstract
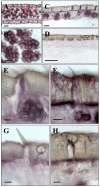
In locusts, olfaction plays a crucial role for initiating and controlling behaviours, including food seeking and aggregation with conspecifics, which underlie the agricultural pest capacity of the animals. In this context, the molecular basis of olfaction in these insects is of particular interest. Here, we have identified genes of two orthopteran species, Locusta migratoria and Schistocera gregaria, which encode the olfactory receptor co-receptor (Orco). It was found that the sequences of LmigOrco and SgreOrco share a high degree of identity to each other and also to Orco proteins from different insect orders. The Orco-expressing cells in the antenna of S. gregaria and L. migratoria were visualized by in situ hybridization. Orco expression could be assigned to clusters of cells in sensilla basiconica and few cells in sensilla trichodea, most likely representing olfactory sensory neurons. No Orco-positive cells were detected in sensilla coeloconica and sensilla chaetica. Orco expression was found already in all nymphal stages and was verified in some other tissues which are equipped with chemosensory hairs (mouthparts, tarsi, wings). Together, the results support the notion for a decisive role of Orco in locust olfaction.
Keywords: Orco; gene expression; in situ hybridization.; locust; olfaction.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures





References
-
- Lomer CJ, Bateman RP, Johnson DL, Langewald J, Thomas M. Biological control of locusts and grasshoppers. Annu Rev Entomol. 2001;46:667–702. - PubMed
-
- Hassanali A, Njagi PG, Bashir MO. Chemical ecology of locusts and related acridids. Annu Rev Entomol. 2005;50:223–45. - PubMed
-
- Ochieng SA, Hansson BS. Responses of olfactory receptor neurones to behaviourally important odours in gregarious and solitarious desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Physiol Entomol. 1999;24:28–36.
-
- Cui X, Wu C, Zhang L. Electrophysiological response patterns of 16 olfactory neurons from the trichoid sensilla to odorant from fecal volatiles in the locust, locusta migratoria manilensis. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2011;77:45–57. - PubMed
-
- Ochieng SA, Hallberg E, Hansson BS. Fine structure and distribution of antennal sensilla of the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria (Orthoptera: Acrididae) Cell Tissue Res. 1998;291:525–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

