The impact of contingency management on quality of life among cocaine abusers with and without alcohol dependence
- PMID: 22211346
- PMCID: PMC3621092
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1521-0391.2011.00185.x
The impact of contingency management on quality of life among cocaine abusers with and without alcohol dependence
Abstract
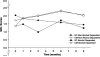
The use of quality of life (QOL) measures in substance abuse treatment research is important because it may lead to a broader understanding of patients' health status and effects of interventions. Despite the high rates of comorbid cocaine and alcohol use disorders, little is known about the QOL of this population, and even less about the impact of an efficacious behavioral treatment, contingency management (CM), on QOL. In this study, data from three clinical trials were retrospectively analyzed to examine QOL in outpatient cocaine abusers with and without alcohol dependence (AD) and the impact of CM on QOL over time as a function of AD status. Patients were randomized to standard care (n = 115) or standard care plus CM (n = 278) for 12 weeks. QOL was assessed at baseline and Months 1, 3, 6, and 9. At treatment initiation, AD patients had lower QOL total scores and they scored lower on several subscale scores than those without AD. CM treatment was associated with improvement in QOL regardless of AD status. These data suggest that CM produces benefits that go beyond substance abuse outcomes, and they support the use of QOL indexes to capture information related to treatment outcomes.
Copyright © American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry.
Figures
References
-
- Helzer JE, Pryzbeck TR. The co-occurrence of alcoholism with other psychiatric disorders in the general population and its impact on treatment. J Stud Alcohol. 1988;49:219–224. - PubMed
-
- Carroll KM, Rounsaville BJ, Bryant KJ. Alcoholism in treatment-seeking cocaine abusers: Clinical and prognostic significance. J Stud Alcohol. 1993;54:199–208. - PubMed
-
- Heil SH, Badger GJ, Higgins ST. Alcohol dependence among cocaine-dependent outpatients: Demographics, drug use, treatment outcome and other characteristics. J Stud Alcohol. 2001;62:14–22. - PubMed
-
- Higgins ST, Budney AJ, Bickel WK, Foerg FE, Badger GJ. Alcohol dependence and simultaneous cocaine and alcohol use in cocaine-dependent patients. J Addict Dis. 1994;13:177–189. - PubMed
-
- Brady KT, Sonne S, Randall CL, Adinnof B, Malcolm R. Features of cocaine dependence with concurrent alcohol abuse. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1995;39:69–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 DA013444/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DA023918/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32-AA07290/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA024667/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA009241/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA021567/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA024667/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR006192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA021567/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA022739/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AA003510/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA027615/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA13444/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA027615/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA018883/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21-DA021836/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA014618/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA022739/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR06192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AA007290/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA018883/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA016855/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA021836/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA14618/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P60-AA03510/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DA023918/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50-DA09241/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical