A randomized comparison of two prophylaxis regimens and a paired comparison of on-demand and prophylaxis treatments in hemophilia A management
- PMID: 22212248
- PMCID: PMC3488301
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04611.x
A randomized comparison of two prophylaxis regimens and a paired comparison of on-demand and prophylaxis treatments in hemophilia A management
Abstract
Background: Prophylaxis with factor (F)VIII is considered the optimal treatment for managing hemophilia A patients without inhibitors.
Objectives: To compare the efficacy of two prophylaxis regimens (primary outcome) and of on-demand and prophylaxis treatments (secondary outcome), and to continue the evaluation of immunogenicity and overall safety of the ADVATE Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant), Plasma/Albumin Free Method (rAHF-PFM).
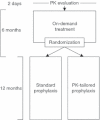
Patients/methods: Previously on-demand-treated patients aged 7-59 years (n = 66) with FVIII levels ≤ 2% received 6 months of on-demand treatment and then were randomized to 12 months of either standard (20-40 IU kg(-1) every other day) or pharmacokinetic (PK)-tailored (20-80 IU kg(-1) every third day) prophylaxis, both regimens intended to maintain FVIII trough levels at or above 1%. Efficacy was evaluated in terms of annualized bleeding rates (ABRs). As subjects were first treated on-demand and then on prophylaxis, statistical comparisons between these treatments were paired.
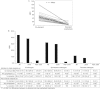
Results: Twenty-two (33.3%) subjects on prophylaxis experienced no bleeding episodes, whereas none treated on-demand were free from an episode of bleeding. ABRs for the two prophylaxis regimens were comparable, whereas differences between on-demand and either prophylaxis were statistically significant (P < 0.0001): median (interquartile range [IQR]) ABRs were 43.9 (21.9), 1.0 (3.5), 2.0 (6.9) and 1.1 (4.9) during on-demand treatment, standard, PK-tailored and any prophylaxis, respectively. There were no differences in FVIII consumption or adverse event rates between prophylaxis regimens. No subject developed FVIII inhibitors.
Conclusions: The present study demonstrates comparable safety and effectiveness for two prophylaxis regimens and that prophylaxis significantly reduces bleeding compared with on-demand treatment. PK-tailored prophylaxis offers an alternative to standard prophylaxis for the prevention of bleeding.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00243386.
© 2011 International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis.
Figures

References
-
- Aledort LM, Haschmeyer RH, Pettersson H. A longitudinal study of orthopaedic outcomes for severe factor-VIII-deficient haemophiliacs. The Orthopaedic Outcome Study Group. J Intern Med. 1994;236:391–9. - PubMed
-
- Lofqvist T, Nilsson IM, Berntorp E, Pettersson H. Haemophilia prophylaxis in young patients – a long-term follow-up. J Intern Med. 1997;241:395–400. - PubMed
-
- Gringeri A, Lundin B, von Mackensen S, Mantovani L, Mannucci PM ESPRIT Study Group. A randomized clinical trial of prophylaxis in children with hemophilia A (the ESPRIT Study) J Thromb Haemost. 2011;9:700–10. - PubMed
-
- National Hemophilia Foundation. MASAC Recommendation Concerning Prophylaxis (Regular Administration of Clotting Factor Concentrate to Prevent Bleeding) National Hemophilia Foundation (NSF); 2007. Apr 11. Report No.: MASAC 179.
-
- Blanchette VS, Shapiro AD, Liesner RJ, Hernández Navarro F, Warrier I, Schroth PC, Spotts G, Ewenstein BM. Plasma and albumin free recombinant factor VIII (rAHF-PFM): pharmacokinetics, efficacy and safety in previously treated pediatric patients. J Thromb Haemost. 2008;6:1319–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

