Pro-inflammatory cytokine-stimulated first trimester decidual cells enhance macrophage-induced apoptosis of extravillous trophoblasts
- PMID: 22212249
- PMCID: PMC3406179
- DOI: 10.1016/j.placenta.2011.12.007
Pro-inflammatory cytokine-stimulated first trimester decidual cells enhance macrophage-induced apoptosis of extravillous trophoblasts
Abstract
Objective: As human blastocyst-derived extravillous trophoblasts (EVTs) invade the early decidua, they are positioned to interact with immune cells and resident decidual cells, and remodel spiral arteries into high capacity vessels that increase blood flow to the developing fetal-placental unit. Shallow EVT invasion elicits incomplete vascular transformation and reduces uteroplacental blood flow that presages adverse pregnancy outcomes. Excess macrophages in the decidua induce EVT apoptosis via tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) secretion. Our previous observation that pro-inflammatory cytokines enhance neutrophil and macrophage activator granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) expression in first trimester decidual cells is now extended to include: (1) the specific macrophage activator M-CSF; (2) macrophage activation and subsequent enhancement of EVT apoptosis by both GM-CSF and M-CSF.
Study design: Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay assessed M-CSF expression in first trimester decidual cells incubated with interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) or TNF-α. Peripheral monocyte-derived macrophages pre-incubated with conditioned media from decidual cell cultures were co-cultured with a first trimester EVT cell line, HTR-8/SVneo cells. Macrophage activation was examined and EVT apoptosis evaluated by DNA fragmentation, caspase activation and cell membrane asymmetry.
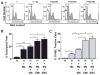
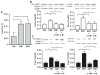
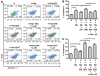
Results: IL-1β or TNF-α significantly enhanced M-CSF expression in first trimester decidual cells. The conditioned media from these cultures activates macrophages, which promote caspase 3/7-dependent EVT apoptosis with antibodies against GM-CSF or M-CSF blocking this effect.
Conclusions: Pro-inflammatory cytokines increases synthesis of M-CSF in first trimester decidual cells. Both GM-CSF and M-CSF activate macrophages, which initiate caspase-dependent EVT apoptosis.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors disclose any conflict of interest.
Figures
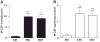

Similar articles
-
Triiodothyronine regulates angiogenic growth factor and cytokine secretion by isolated human decidual cells in a cell-type specific and gestational age-dependent manner.Hum Reprod. 2014 Jun;29(6):1161-72. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deu046. Epub 2014 Mar 13. Hum Reprod. 2014. PMID: 24626803 Free PMC article.
-
Production of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor by human trophoblast cells and by decidual large granular lymphocytes.Hum Reprod. 1994 Sep;9(9):1660-9. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a138769. Hum Reprod. 1994. PMID: 7530725
-
Differential regulation of colony stimulating factor 1 and macrophage migration inhibitory factor expression by inflammatory cytokines in term human decidua: implications for macrophage trafficking at the fetal-maternal interface.Biol Reprod. 2007 Mar;76(3):433-9. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.106.054189. Epub 2006 Nov 15. Biol Reprod. 2007. PMID: 17108334
-
The role of decidual cells in uterine hemostasis, menstruation, inflammation, adverse pregnancy outcomes and abnormal uterine bleeding.Hum Reprod Update. 2016 Jun;22(4):497-515. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmw004. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Hum Reprod Update. 2016. PMID: 26912000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Placental Extravillous Trophoblasts by the Maternal Uterine Environment.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 13;9:2597. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02597. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30483261 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of CX3CL1 Expression in Human First-Trimester Decidual Cells: Implications for Preeclampsia.Reprod Sci. 2019 Sep;26(9):1256-1265. doi: 10.1177/1933719118815592. Epub 2019 Jan 3. Reprod Sci. 2019. PMID: 30606080 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Macrophages in Pregnancy and Related Complications.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2019 Oct;67(5):295-309. doi: 10.1007/s00005-019-00552-7. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2019. PMID: 31286151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
M1/M2 macrophage polarity in normal and complicated pregnancy.Front Immunol. 2014 Nov 24;5:606. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00606. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25505471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of Decidual Macrophage Polarization by Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor Derived from First-Trimester Decidual Cells: Implication in Preeclampsia.Am J Pathol. 2016 May;186(5):1258-66. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.12.021. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Am J Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26970370 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Obesity and the Uterine Immune Cell Landscape: The Shaping Role of Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 27;21(11):3776. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113776. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32471078 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Trundley A, Moffett A. Human uterine leukocytes and pregnancy. Tissue Antigens. 2004;63(1):1–12. - PubMed
-
- Pijnenborg R, Bland JM, Robertson WB, Brosens I. Uteroplacental arterial changes related to interstitial trophoblast migration in early human pregnancy. Placenta. 1983;4(4):397–413. - PubMed
-
- Kaufmann P, Black S, Huppertz B. Endovascular trophoblast invasion: implications for the pathogenesis of intrauterine growth retardation and preeclampsia. Biol Reprod. 2003;69(1):1–7. - PubMed
-
- Straszewski-Chavez SL, Abrahams VM, Mor G. The role of apoptosis in the regulation of trophoblast survival and differentiation during pregnancy. Endocr Rev. 2005;26(7):877–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

