Randomized trial of exercise effect on intrahepatic triglyceride content and lipid kinetics in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 22213436
- PMCID: PMC3337888
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.25548
Randomized trial of exercise effect on intrahepatic triglyceride content and lipid kinetics in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
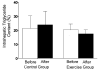
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alterations in hepatic lipoprotein kinetics are common metabolic complications associated with obesity. Lifestyle modification involving diet-induced weight loss and regular exercise decreases intrahepatic triglyceride (IHTG) content and very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) triglyceride (TG) secretion rate. The aim of this study was to evaluate the weight loss-independent effect of following the physical activity guidelines recommended by the Department of Health and Human Services on IHTG content and VLDL kinetics in obese persons with NAFLD. Eighteen obese people (body mass index [BMI]: 38.1 ± 4.6 kg/m(2)) with NAFLD were randomized to 16 weeks of exercise training (45%-55% VO(2peak) , 30-60 minutes × 5 days/week; n = 12) or observation (control; n = 6). Magnetic resonance spectroscopy and stable isotope tracer infusions in conjunction with compartmental modeling were used to evaluate IHTG content and hepatic VLDL-TG and apolipoprotein B-100 (apoB-100) secretion rates. Exercise training resulted in a 10.3% ± 4.6% decrease in IHTG content (P < 0.05), but did not change total body weight (103.1 ± 4.2 kg before and 102.9 ± 4.2 kg after training) or percent body fat (38.9% ± 2.1% before and 39.2% ± 2.1% after training). Exercise training did not change the hepatic VLDL-TG secretion rate (17.7 ± 3.9 μmol/min before and 16.8 ± 5.4 μmol/min after training) or VLDL-apoB-100 secretion rate (1.5 ± 0.5 nmol/min before and 1.6 ± 0.6 nmol/min after training).
Conclusion: Following the Department of Health and Human Services recommended physical activity guidelines has small but beneficial effects on IHTG content, but does not improve hepatic lipoprotein kinetics in obese persons with NAFLD.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00771108.
Copyright © 2012 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Adiels M, Taskinen MR, Packard C, Caslake M, Soro-Paavonen A, Westerbacka J, Vehkavaara S, et al. Overproduction of large VLDL particles is driven by increased liver fat content in man. Diabetologia. 2006;49:755–765. - PubMed
-
- Kantartzis K, Machann J, Schick F, Rittig K, Machicao F, Fritsche A, Haring HU, et al. Effects of a lifestyle intervention in metabolically benign and malign obesity. Diabetologia. 2011;54:864–868. - PubMed
-
- Kantartzis K, Thamer C, Peter A, Machann J, Schick F, Schraml C, Konigsrainer A, et al. High cardiorespiratory fitness is an independent predictor of the reduction in liver fat during a lifestyle intervention in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut. 2009;58:1281–1288. - PubMed
-
- Koot BG, van der Baan-Slootweg OH, Tamminga-Smeulders CL, Rijcken TH, Korevaar JC, van Aalderen WM, Jansen PL, et al. Lifestyle intervention for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: prospective cohort study of its efficacy and factors related to improvement. Arch Dis Child. 2011;96:669–674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- DK37948/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK78738/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK052574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK078738/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR24992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK052574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HD57796/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD057796/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK037948/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR024994/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK56341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000450/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
