The role of adjuvant in mediating antigen structure and stability
- PMID: 22213631
- PMCID: PMC6140791
- DOI: 10.1002/jps.23039
The role of adjuvant in mediating antigen structure and stability
Abstract
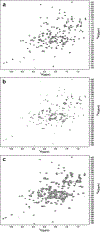
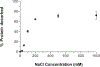
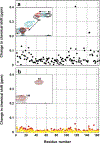
The purpose of this study was to probe the fate of a model antigen, a cysteine-free mutant of bacteriophage T4 lysozyme, to the level of fine structural detail, as a consequence of its interaction with an aluminum (Al)-containing adjuvant. Fluorescence spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry were used to compare the thermal stability of the protein in solution versus adsorbed onto an Al-containing adjuvant. Differences in accessible hydrophobic surface areas were investigated using an extrinsic fluorescence probe, 8-Anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid (ANS). As has been observed with other model antigens, the apparent thermal stability of the protein decreased following adsorption onto the adjuvant. ANS spectra suggested that adsorption onto the adjuvant caused an increase in exposure of hydrophobic regions of the protein. Electrostatic interactions drove the adsorption, and disruption of these interactions with high ionic strength buffers facilitated the collection of two-dimensional (15) N heteronuclear single quantum coherence nuclear magnetic resonance data of protein released from the adjuvant. Although the altered stability of the adsorbed protein suggested changes to the protein's structure, the fine structure of the desorbed protein was nearly identical to the protein's structure in the adjuvant-free formulation. Thus, the adjuvant-induced changes to the protein that were responsible for the reduced thermal stability were not observed upon desorption.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
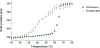

Similar articles
-
Effects of adsorption to aluminum salt adjuvants on the structure and stability of model protein antigens.J Biol Chem. 2005 Apr 8;280(14):13406-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500687200. Epub 2005 Jan 31. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15684430
-
Elucidating the mechanisms of protein antigen adsorption to the CAF/NAF liposomal vaccine adjuvant systems: effect of charge, fluidity and antigen-to-lipid ratio.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Aug;1838(8):2001-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.04.013. Epub 2014 Apr 25. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24769435
-
Contribution of electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions to the adsorption of proteins by aluminium-containing adjuvants.Vaccine. 1995 Jan;13(1):41-4. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(95)80009-3. Vaccine. 1995. PMID: 7762276
-
Quantitative Analysis of Vaccine Antigen Adsorption to Aluminum Adjuvant Using an Automated High-Throughput Method.PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2018 Mar-Apr;72(2):149-162. doi: 10.5731/pdajpst.2017.008250. Epub 2018 Jan 17. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2018. PMID: 29343619
-
Stability of a trivalent recombinant protein vaccine formulation against botulinum neurotoxin during storage in aqueous solution.J Pharm Sci. 2009 Sep;98(9):2970-93. doi: 10.1002/jps.21498. J Pharm Sci. 2009. PMID: 18680175 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Aluminum Adjuvants-'Back to the Future'.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 4;15(7):1884. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071884. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoemulsion-based mucosal adjuvant induces apoptosis in human epithelial cells.Vaccine. 2015 May 5;33(19):2289-2296. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.03.002. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 25817825 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausar SF, Chan J, Hoque W, James O, Jayasundara K, Harper K. Application of extrinsic fluorescence spectroscopy for the high throughput formulation screening of aluminumadjuvanted vaccines. J Pharm Sci 100(2):431–440. - PubMed
-
- Jones LS, Peek LJ, Power J, Markham A, Yazzie B, Middaugh CR. 2005. Effects of adsorption to aluminum salt adjuvants on the structure and stability of model protein antigens. J Biol Chem 280(14):13406–13414. - PubMed
-
- Peek LJ, Martin TT, Elk Nation C, Pegram SA, Middaugh CR.2007. Effects of stabilizers on the destabilization of proteins upon adsorption to aluminum salt adjuvants. J Pharm Sci 96(3):547–557. - PubMed
-
- Matsumura M, Matthews BW. 1989. Control of enzyme activity by an engineered disulfide bond. Science 243(4892):792–794. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

