Plus-end directed myosins accelerate actin filament sliding by single-headed myosin VI
- PMID: 22213699
- PMCID: PMC3327287
- DOI: 10.1002/cm.21002
Plus-end directed myosins accelerate actin filament sliding by single-headed myosin VI
Abstract
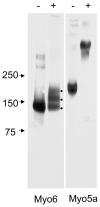
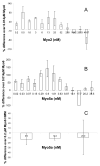
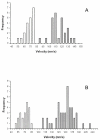
Myosin VI (Myo6) is unique among myosins in that it moves toward the minus (pointed) end of the actin filament. Thus to exert tension on, or move cargo along an actin filament, Myo6 is working against potentially multiple plus (barbed)-end myosins. To test the effect of plus-end motors on Myo6, the gliding actin filament assay was used to assess the motility of single-headed Myo6 in the absence and presence of cardiac myosin II (Myo2) and myosin Va (Myo5a). Myo6 alone exhibited a filament gliding velocities of 60.34 ± 13.68 nm/s. Addition of either Myo2 or Myo5a, at densities below that required to promote plus-end movement resulted in an increase in Myo6 velocity (~100-150% increase). Movement in the presence of these plus-end myosins was minus-end directed as determined using polarity tagged filaments. High densities of Myo2 or Myo5a were required to convert to plus-end directed motility indicating that Myo6 is a potent inhibitor of Myo2 and Myo5a. Previous studies have shown that two-headed Myo6 slows and then stalls in an anchored state under load. Consistent with these studies, velocity of a two headed heavy mero myosin form of Myo6 was unaffected by Myo5a at low densities, and was inhibited at high Myo5a densities.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Restoration of cytoskeletal and membrane tethering defects but not defects in membrane trafficking in the intestinal brush border of mice lacking both myosin Ia and myosin VI.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2015 Sep;72(9):455-76. doi: 10.1002/cm.21238. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2015. PMID: 26286357 Free PMC article.
-
Filopodia formation and endosome clustering induced by mutant plus-end-directed myosin VI.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Feb 14;114(7):1595-1600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1616941114. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28143933 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin-IXb is a single-headed and processive motor.J Biol Chem. 2002 Apr 5;277(14):11679-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111173200. Epub 2002 Jan 18. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11801597
-
Diverse functions of myosin VI in spermiogenesis.Histochem Cell Biol. 2021 Mar;155(3):323-340. doi: 10.1007/s00418-020-01954-x. Epub 2021 Jan 2. Histochem Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33386429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The MYO6 interactome: selective motor-cargo complexes for diverse cellular processes.FEBS Lett. 2019 Jul;593(13):1494-1507. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13486. Epub 2019 Jul 3. FEBS Lett. 2019. PMID: 31206648 Review.
Cited by
-
Myosin motors at neuronal synapses: drivers of membrane transport and actin dynamics.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013 Apr;14(4):233-47. doi: 10.1038/nrn3445. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23481482 Review.
-
Restoration of cytoskeletal and membrane tethering defects but not defects in membrane trafficking in the intestinal brush border of mice lacking both myosin Ia and myosin VI.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2015 Sep;72(9):455-76. doi: 10.1002/cm.21238. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2015. PMID: 26286357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altman D, Sweeney HL, Spudich JA. The mechanism of myosin VI translocation and its load-induced anchoring. Cell. 2004;116:737–49. see comment. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

