Subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant unipolar and bipolar depression
- PMID: 22213770
- PMCID: PMC4423545
- DOI: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.1456
Subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant unipolar and bipolar depression
Abstract
Context: Deep brain stimulation (DBS) may be an effective intervention for treatment-resistant depression (TRD), but available data are limited.
Objective: To assess the efficacy and safety of subcallosal cingulate DBS in patients with TRD with either major depressive disorder (MDD) or bipolar II disorder (BP).
Design: Open-label trial with a sham lead-in phase.
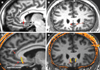
Setting: Academic medical center. Patients Men and women aged 18 to 70 years with a moderate-to-severe major depressive episode after at least 4 adequate antidepressant treatments. Ten patients with MDD and 7 with BP were enrolled from a total of 323 patients screened. Intervention Deep brain stimulation electrodes were implanted bilaterally in the subcallosal cingulate white matter. Patients received single-blind sham stimulation for 4 weeks followed by active stimulation for 24 weeks. Patients then entered a single-blind discontinuation phase; this phase was stopped after the first 3 patients because of ethical concerns. Patients were evaluated for up to 2 years after the onset of active stimulation.
Main outcome measures: Change in depression severity and functioning over time, and response and remission rates after 24 weeks were the primary efficacy end points; secondary efficacy end points were 1 year and 2 years of active stimulation.
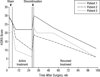
Results: A significant decrease in depression and increase in function were associated with chronic stimulation. Remission and response were seen in 3 patients (18%) and 7 (41%) after 24 weeks (n = 17), 5 (36%) and 5 (36%) after 1 year (n = 14), and 7 (58%) and 11 (92%) after 2 years (n = 12) of active stimulation. No patient achieving remission experienced a spontaneous relapse. Efficacy was similar for patients with MDD and those with BP. Chronic DBS was safe and well tolerated, and no hypomanic or manic episodes occurred. A modest sham stimulation effect was found, likely due to a decrease in depression after the surgical intervention but prior to entering the sham phase.
Conclusions: The findings of this study support the long-term safety and antidepressant efficacy of subcallosal cingulate DBS for TRD and suggest equivalent safety and efficacy for TRD in patients with BP. Trial Registration clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT00367003.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Crown WH, Finkelstein S, Berndt ER, Ling D, Poret AW, Rush AJ, Russell JM. The impact of treatment-resistant depression on health care utilization and costs. J Clin Psychiatry. 2002;63(11):963–971. - PubMed
-
- Mayberg HS, Lozano AM, Voon V, McNeely HE, Seminowicz D, Hamani C, Schwalb JM, Kennedy SH. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron. 2005;45(5):651–660. - PubMed
-
- Lozano AM, Mayberg HS, Giacobbe P, Hamani C, Craddock RC, Kennedy SH. Subcallosal cingulate gyrus deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;64(6):461–467. - PubMed
-
- Malone DA, Jr, Dougherty DD, Rezai AR, Carpenter LL, Friehs GM, Eskandar EN, Rauch SL, Rasmussen SA, Machado AG, Kubu CS, Tyrka AR, Price LH, Stypulkowski PH, Giftakis JE, Rise MT, Malloy PF, Salloway SP, Greenberg BD. Deep brain stimulation of the ventral capsule/ventral striatum for treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;65(4):267–275. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

