Short-term clinicopathological outcome of neoadjuvant chemohormonal therapy comprising complete androgen blockade, followed by treatment with docetaxel and estramustine phosphate before radical prostatectomy in Japanese patients with high-risk localized prostate cancer
- PMID: 22214417
- PMCID: PMC3267659
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7819-10-1
Short-term clinicopathological outcome of neoadjuvant chemohormonal therapy comprising complete androgen blockade, followed by treatment with docetaxel and estramustine phosphate before radical prostatectomy in Japanese patients with high-risk localized prostate cancer
Abstract
Background: To assess the outcome of neoadjuvant chemohormonal therapy comprising complete androgen blockade followed by treatment with docetaxel and estramustine phosphate before radical prostatectomy in Japanese patients with a high risk of localized prostate cancer (PCa).
Methods: Complete androgen blockade followed by 6 cycles of docetaxel (30 mg/m2) with estramustine phosphate (560 mg) were given to 18 PCa patients before radical prostatectomy. Subsequently, the clinical and pathological outcomes were analyzed.
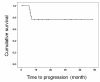
Results: No patients had severe adverse events during chemohormonal therapy, and hence they were treated with radical prostatectomy. Two patients (11.1%) achieved pathological complete response. Surgical margins were negative in all patients. At a median follow-up of 18 months, 14 patients (77.8%) were disease-free without PSA recurrence. All 4 patients with PSA recurrence had pathologic T3b or T4 disease and 3 of these 4 patients had pathologic N1 disease.
Conclusion: We found that neoadjuvant chemohormonal therapy with complete androgen blockade followed by treatment with docetaxel and estramustine phosphate before radical prostatectomy was safe, feasible, and associated with favorable pathological outcomes in patients with a high risk of localized PCa.
References
-
- D'Amico AV, Whittington R, Malkowicz SB, Schultz D, Blank K, Broderick GA, Tomaszewski JE, Renshaw AA, Kaplan I, Beard CJ, Wein A. Biochemical outcome after radical prostatectomy, external beam radiation therapy, or interstitial radiation therapy for clinically localized prostate cancer. Jama. 1998;280:969–974. doi: 10.1001/jama.280.11.969. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous