Cytokines and brain excitability
- PMID: 22214786
- PMCID: PMC3547977
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2011.12.002
Cytokines and brain excitability
Abstract
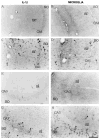
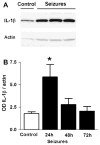
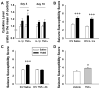
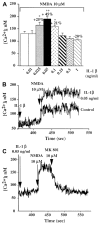
Cytokines are molecules secreted by peripheral immune cells, microglia, astrocytes and neurons in the central nervous system. Peripheral or central inflammation is characterized by an upregulation of cytokines and their receptors in the brain. Emerging evidence indicates that pro-inflammatory cytokines modulate brain excitability. Findings from both the clinical literature and from in vivo and in vitro laboratory studies suggest that cytokines can increase seizure susceptibility and may be involved in epileptogenesis. Cellular mechanisms that underlie these effects include upregulation of excitatory glutamatergic transmission and downregulation of inhibitory GABAergic transmission.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Akin D, Ravizza T, Maroso M, Carcak N, Eryigit T, Vanzulli I, Aker RG, Vezzani A, Onat FY. IL-1beta is induced in reactive astrocytes in the somatosensory cortex of rats with genetic absence epilepsy at the onset of spike-and-wave discharges, and contributes to their occurrence. Neurobiol Dis. 2011;44:259–269. - PubMed
-
- Albensi BC, Mattson MP. Evidence for the involvement of TNF and NF-kappaB in hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Synapse. 2000;35:151–159. - PubMed
-
- Allan SM, Tyrrell PJ, Rothwell NJ. Interleukin-1 and neuronal injury. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:629–640. - PubMed
-
- Aronica E, Crino PB. Inflammation in epilepsy: clinical observations. Epilepsia. 2011;52(Suppl 3):26–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

