Monocyte tissue factor-dependent activation of coagulation in hypercholesterolemic mice and monkeys is inhibited by simvastatin
- PMID: 22214850
- PMCID: PMC3266787
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI58969
Monocyte tissue factor-dependent activation of coagulation in hypercholesterolemic mice and monkeys is inhibited by simvastatin
Abstract
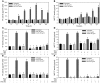
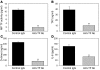
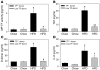
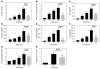
Hypercholesterolemia is a major risk factor for atherosclerosis. It also is associated with platelet hyperactivity, which increases morbidity and mortality from cardiovascular disease. However, the mechanisms by which hypercholesterolemia produces a procoagulant state remain undefined. Atherosclerosis is associated with accumulation of oxidized lipoproteins within atherosclerotic lesions. Small quantities of oxidized lipoproteins are also present in the circulation of patients with coronary artery disease. We therefore hypothesized that hypercholesterolemia leads to elevated levels of oxidized LDL (oxLDL) in plasma and that this induces expression of the procoagulant protein tissue factor (TF) in monocytes. In support of this hypothesis, we report here that oxLDL induced TF expression in human monocytic cells and monocytes. In addition, patients with familial hypercholesterolemia had elevated levels of plasma microparticle (MP) TF activity. Furthermore, a high-fat diet induced a time-dependent increase in plasma MP TF activity and activation of coagulation in both LDL receptor-deficient mice and African green monkeys. Genetic deficiency of TF in bone marrow cells reduced coagulation in hypercholesterolemic mice, consistent with a major role for monocyte-derived TF in the activation of coagulation. Similarly, a deficiency of either TLR4 or TLR6 reduced levels of MP TF activity. Simvastatin treatment of hypercholesterolemic mice and monkeys reduced oxLDL, monocyte TF expression, MP TF activity, activation of coagulation, and inflammation, without affecting total cholesterol levels. Our results suggest that the prothrombotic state associated with hypercholesterolemia is caused by oxLDL-mediated induction of TF expression in monocytes via engagement of a TLR4/TLR6 complex.
Figures





Comment in
-
Teaching an old dog new tricks: potential antiatherothrombotic use for statins.J Clin Invest. 2012 Feb;122(2):478-81. doi: 10.1172/JCI61857. Epub 2012 Jan 3. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 22214843 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Teaching an old dog new tricks: potential antiatherothrombotic use for statins.J Clin Invest. 2012 Feb;122(2):478-81. doi: 10.1172/JCI61857. Epub 2012 Jan 3. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 22214843 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperlipidemia, tissue factor, coagulation, and simvastatin.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2014 Apr;24(3):95-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Sep 7. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2014. PMID: 24016468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet tissue factor activity and membrane cholesterol are increased in hypercholesterolemia and normalized by rosuvastatin, but not by atorvastatin.Atherosclerosis. 2017 Feb;257:164-171. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.12.019. Epub 2016 Dec 16. Atherosclerosis. 2017. PMID: 28142075 Clinical Trial.
-
Colchicine inhibits the prothrombotic effects of oxLDL in human endothelial cells.Vascul Pharmacol. 2021 Apr;137:106822. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2020.106822. Epub 2020 Nov 21. Vascul Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33232770
-
Sources of tissue factor that contribute to thrombosis after rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque.Thromb Res. 2012 May;129 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S30-3. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2012.02.026. Epub 2012 Mar 22. Thromb Res. 2012. PMID: 22444158 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of simvastatin on tissue factor pathway of blood coagulation in STATCOPE (Simvastatin in the prevention of COPD exacerbations) trial.J Thromb Haemost. 2021 Jul;19(7):1709-1717. doi: 10.1111/jth.15282. Epub 2021 Apr 12. J Thromb Haemost. 2021. PMID: 33638931 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
(18)F-FDG PET imaging of murine atherosclerosis: association with gene expression of key molecular markers.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50908. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050908. Epub 2012 Nov 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23226424 Free PMC article.
-
Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: pathophysiological, genetic, and therapeutic insights: a consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel.Eur Heart J. 2020 Jun 21;41(24):2313-2330. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz962. Eur Heart J. 2020. PMID: 32052833 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Monocyte bioenergetics: An immunometabolic perspective in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis.Cell Rep Med. 2024 May 21;5(5):101564. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101564. Epub 2024 May 10. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 38733988 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk of ferroptosis and oxidative stress in infectious diseases.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Dec 7;10:1315935. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1315935. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38131014 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stamler J, Wentworth D, Neaton JD. Is relationship between serum cholesterol and risk of premature death from coronary heart disease continuous and graded? Findings in 356,222 primary screenees of the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial (MRFIT). JAMA. 1986;256(20):2823–2828. doi: 10.1001/jama.1986.03380200061022. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL087203/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL095096/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-HL087203/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086674/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00-HL088528/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095096/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL099175/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1F32-HL099175-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL092125/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL091797/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL086674/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-HL006350/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL006350/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092125/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL088528/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

