Muscle-derived stem/progenitor cell dysfunction limits healthspan and lifespan in a murine progeria model
- PMID: 22215083
- PMCID: PMC3272577
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms1611
Muscle-derived stem/progenitor cell dysfunction limits healthspan and lifespan in a murine progeria model
Abstract
With ageing, there is a loss of adult stem cell function. However, there is no direct evidence that this has a causal role in ageing-related decline. We tested this using muscle-derived stem/progenitor cells (MDSPCs) in a murine progeria model. Here we show that MDSPCs from old and progeroid mice are defective in proliferation and multilineage differentiation. Intraperitoneal administration of MDSPCs, isolated from young wild-type mice, to progeroid mice confer significant lifespan and healthspan extension. The transplanted MDSPCs improve degenerative changes and vascularization in tissues where donor cells are not detected, suggesting that their therapeutic effect may be mediated by secreted factor(s). Indeed, young wild-type-MDSPCs rescue proliferation and differentiation defects of aged MDSPCs when co-cultured. These results establish that adult stem/progenitor cell dysfunction contributes to ageing-related degeneration and suggests a therapeutic potential of post-natal stem cells to extend health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors, except J.H., declare no competing financial interests. J.H. receives consulting fees from Cook MyoSite.
Figures
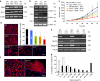



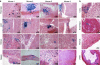



References
-
- Kirkwood T. B. Understanding the odd science of aging. Cell 120, 437–447 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Sharpless N. E. & DePinho R. A. How stem cells age and why this makes us grow old. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 703–713 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Rossi D. J., Jamieson C. H. & Weissman I. L. Stems cells and the pathways to aging and cancer. Cell 132, 681–696 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

