HIV-1 infection alters CD4+ memory T-cell phenotype at the site of disease in extrapulmonary tuberculosis
- PMID: 22215422
- PMCID: PMC3298896
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.201141927
HIV-1 infection alters CD4+ memory T-cell phenotype at the site of disease in extrapulmonary tuberculosis
Abstract
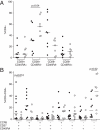
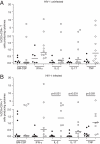
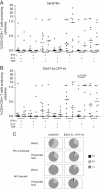
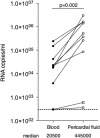
HIV-1-infected people have an increased risk of developing extrapulmonary tuberculosis (TB), the immunopathogenesis of which is poorly understood. Here, we conducted a detailed immunological analysis of human pericardial TB, to determine the effect of HIV-1 co-infection on the phenotype of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB)-specific memory T cells and the role of polyfunctional T cells at the disease site, using cells from pericardial fluid and blood of 74 patients with (n = 50) and without (n = 24) HIV-1 co-infection. The MTB antigen-induced IFN-γ response was elevated at the disease site, irrespective of HIV-1 status or antigenic stimulant. However, the IFN-γ ELISpot showed no clear evidence of increased numbers of antigen-specific cells at the disease site except for ESAT-6 in HIV-1 uninfected individuals (p = 0.009). Flow cytometric analysis showed that CD4+ memory T cells in the pericardial fluid of HIV-1-infected patients were of a less differentiated phenotype, with the presence of polyfunctional CD4+ T cells expressing TNF, IL-2 and IFN-γ. These results indicate that HIV-1 infection results in altered phenotype and function of MTB-specific CD4+ T cells at the disease site, which may contribute to the increased risk of developing TB at all stages of HIV-1 infection.
Figures

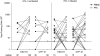
References
-
- Meintjes G, Wilkinson RJ. Undiagnosed active tuberculosis in HIV-infected patients commencing antiretroviral therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010;51:830–832. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Global tuberculosis control: key findings from the December 2009 WHO report. Wkly Epidemiol. Rec. 2010;85:69–80. - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson RJ, Vordermeier HM, Wilkinson KA, Sjolund A, Moreno C, Pasvol G, Ivanyi J. Peptide-specific T cell response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis: clinical spectrum, compartmentalization, and effect of chemotherapy. J. Infect. Dis. 1998;178:760–768. - PubMed
-
- Pathan AA, Wilkinson KA, Klenerman P, McShane H, Davidson RN, Pasvol G, Hill AV, et al. Direct ex vivo analysis of antigen-specific IFN-gamma-secreting CD4 T cells in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected individuals: associations with clinical disease state and effect of treatment. J. Immunol. 2001;167:5217–5225. - PubMed
-
- Mayosi BM, Wiysonge CS, Ntsekhe M, Gumedze F, Volmink JA, Maartens G, Aje A, et al. Mortality in patients treated for tuberculous pericarditis in sub-Saharan Africa. South Afr. Med. J. 2008;98:36–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

