Saccharomyces cerevisiae NineTeen complex (NTC)-associated factor Bud31/Ycr063w assembles on precatalytic spliceosomes and improves first and second step pre-mRNA splicing efficiency
- PMID: 22215661
- PMCID: PMC3285318
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.298547
Saccharomyces cerevisiae NineTeen complex (NTC)-associated factor Bud31/Ycr063w assembles on precatalytic spliceosomes and improves first and second step pre-mRNA splicing efficiency
Abstract
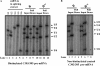
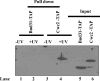
Pre-mRNA splicing occurs in spliceosomes whose assembly and activation are critical for splice site selection and catalysis. The highly conserved NineTeen complex protein complex stabilizes various snRNA and protein interactions early in the spliceosome assembly pathway. Among several NineTeen complex-associated proteins is the nonessential protein Bud31/Ycr063w, which is also a component of the Cef1p subcomplex. A role for Bud31 in pre-mRNA splicing is implicated by virtue of its association with splicing factors, but its specific functions and spliceosome interactions are uncharacterized. Here, using in vitro splicing assays with extracts from a strain lacking Bud31, we illustrate its role in efficient progression to the first catalytic step and its requirement for the second catalytic step in reactions at higher temperatures. Immunoprecipitation of functional epitope-tagged Bud31 from in vitro reactions showed that its earliest association is with precatalytic B complex and that the interaction continues in catalytically active complexes with stably bound U2, U5, and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. In complementary experiments, wherein precatalytic spliceosomes are selected from splicing reactions, we detect the occurrence of Bud31. Cross-linking of proteins to pre-mRNAs with a site-specific 4-thio uridine residue at the -3 position of exon 1 was tested in reactions with WT and bud31 null extracts. The data suggest an altered interaction between a ∼25-kDa protein and this exonic residue of pre-mRNAs in the arrested bud31 null spliceosomes. These results demonstrate the early spliceosomal association of Bud31 and provide plausible functions for this factor in stabilizing protein interactions with the pre-mRNA.
Figures





References
-
- Chan S. P., Kao D. I., Tsai W. Y., Cheng S. C. (2003) The Prp19p-associated complex in spliceosome activation. Science 302, 279–282 - PubMed
-
- Fabrizio P., Dannenberg J., Dube P., Kastner B., Stark H., Urlaub H., Lührmann R. (2009) The evolutionarily conserved core design of the catalytic activation step of the yeast spliceosome. Mol. Cell 36, 593–608 - PubMed
-
- Chen H. R., Jan S. P., Tsao T. Y., Sheu Y. J., Banroques J., Cheng S. C. (1998) Snt309p, a component of the Prp19p-associated complex that interacts with Prp19p and associates with the spliceosome simultaneously with or immediately after dissociation of U4 in the same manner as Prp19p. Mol. Cell Biol. 18, 2196–2204 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tsai W. Y., Chow Y. T., Chen H. R., Huang K. T., Hong R. I., Jan S. P., Kuo N. Y., Tsao T. Y., Chen C. H., Cheng S. C. (1999) Cef1p is a component of the Prp19p-associated complex and essential for pre-mRNA splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 9455–9462 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

