Insights into role of bromodomain, testis-specific (Brdt) in acetylated histone H4-dependent chromatin remodeling in mammalian spermiogenesis
- PMID: 22215678
- PMCID: PMC3307259
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.288167
Insights into role of bromodomain, testis-specific (Brdt) in acetylated histone H4-dependent chromatin remodeling in mammalian spermiogenesis
Abstract
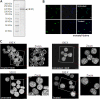
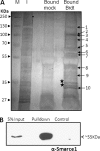
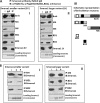
Mammalian spermiogenesis is of considerable biological interest especially due to the unique chromatin remodeling events that take place during spermatid maturation. Here, we have studied the expression of chromatin remodeling factors in different spermatogenic stages and narrowed it down to bromodomain, testis-specific (Brdt) as a key molecule participating in chromatin remodeling during rat spermiogenesis. Our immunocytochemistry experiments reveal that Brdt colocalizes with acetylated H4 in elongating spermatids. Remodeling assays showed an acetylation-dependent but ATP-independent chromatin reorganization property of Brdt in haploid round spermatids. Furthermore, Brdt interacts with Smarce1, a member of the SWI/SNF family. We have studied the genomic organization of smarce1 and identified that it has two splice variants expressed during spermatogenesis. The N terminus of Brdt is involved in the recognition of Smarce1 as well as in the reorganization of hyperacetylated round spermatid chromatin. Interestingly, the interaction between Smarce1 and Brdt increases dramatically upon histone hyperacetylation both in vitro and in vivo. Thus, our results indicate this interaction to be a vital step in the chromatin remodeling process during mammalian spermiogenesis.
Figures








References
-
- Kornberg R. D. (1974) Chromatin structure. A repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science 184, 868–871 - PubMed
-
- Luger K., Mäder A. W., Richmond R. K., Sargent D. F., Richmond T. J. (1997) Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 Å resolution. Nature 389, 251–260 - PubMed
-
- Peterson C. L., Laniel M. A. (2004) Histones and histone modifications. Curr. Biol. 14, R546–R551 - PubMed
-
- Shahbazian M. D., Grunstein M. (2007) Functions of site-specific histone acetylation and deacetylation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 76, 75–100 - PubMed
-
- Jenuwein T., Allis C. D. (2001) Translating the histone code. Science 293, 1074–1080 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

