Novel patient cell-based HTS assay for identification of small molecules for a lysosomal storage disease
- PMID: 22216298
- PMCID: PMC3244463
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029504
Novel patient cell-based HTS assay for identification of small molecules for a lysosomal storage disease
Abstract
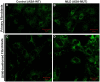
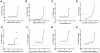
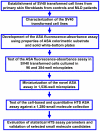
Small molecules have been identified as potential therapeutic agents for lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs), inherited metabolic disorders caused by defects in proteins that result in lysosome dysfunctional. Some small molecules function assisting the folding of mutant misfolded lysosomal enzymes that are otherwise degraded in ER-associated degradation. The ultimate result is the enhancement of the residual enzymatic activity of the deficient enzyme. Most of the high throughput screening (HTS) assays developed to identify these molecules are single-target biochemical assays. Here we describe a cell-based assay using patient cell lines to identify small molecules that enhance the residual arylsulfatase A (ASA) activity found in patients with metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD), a progressive neurodegenerative LSD. In order to generate sufficient cell lines for a large scale HTS, primary cultured fibroblasts from MLD patients were transformed using SV40 large T antigen. These SV40 transformed (SV40t) cells showed to conserve biochemical characteristics of the primary cells. Using a specific colorimetric substrate para-nitrocatechol sulfate (pNCS), detectable ASA residual activity were observed in primary and SV40t fibroblasts from a MLD patient (ASA-I179S) cultured in multi-well plates. A robust fluorescence ASA assay was developed in high-density 1,536-well plates using the traditional colorimetric pNCS substrate, whose product (pNC) acts as "plate fluorescence quencher" in white solid-bottom plates. The quantitative cell-based HTS assay for ASA generated strong statistical parameters when tested against a diverse small molecule collection. This cell-based assay approach can be used for several other LSDs and genetic disorders, especially those that rely on colorimetric substrates which traditionally present low sensitivity for assay-miniaturization. In addition, the quantitative cell-based HTS assay here developed using patient cells creates an opportunity to identify therapeutic small molecules in a disease-cellular environment where potentially disrupted pathways are exposed and available as targets.
© 2011 Geng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- An WF, Tolliday N. Cell-based assays for high-throughput screening. Mol Biotechnol. 2010;45:180–186. - PubMed
-
- Hampton SL, Kinnaird AI. Genetic interventions in mammalian cells; applications and uses in high-throughput screening and drug discovery. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2010;26:43–55. - PubMed
-
- Smid BE, Aerts JM, Boot RG, Linthorst GE, Hollak CE. Pharmacological small molecules for the treatment of lysosomal storage disorders. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010;19:1367–1379. - PubMed
-
- Meikle PJ, Hopwood JJ, Clague AE, Carey WF. Prevalence of lysosomal storage disorders. JAMA. 1999;281:249–254. - PubMed
-
- Grabowski GA, Hopkin RJ. Enzyme therapy for lysosomal storage disease: principles, practice, and prospects. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2003;4:403–436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

