Heregulin β-1 induces loss of cell-cell contact and enhances expression of MUC1 at the cell surface in HCC2998 and MKN45-1 cells
- PMID: 22216327
- PMCID: PMC3245292
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029599
Heregulin β-1 induces loss of cell-cell contact and enhances expression of MUC1 at the cell surface in HCC2998 and MKN45-1 cells
Abstract
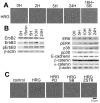
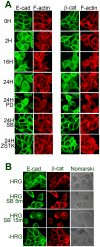
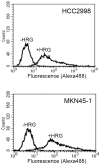
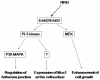
Signal transduction and cell responses after stimulation with heregulin β-1 (HRG) are examined in HCC2998 and MKN45-1 cells, which have been used for a model system to study the formation of signet ring carcinomas, one of poorly differentiated adenocarcinomas. HRG stimulation causes rounding of the cells, responding to HRG. The adherens junction, which is present in the control cells, is disrupted and cell-cell interaction is lost after stimulation. Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol (PI)-3 kinase or p38 MAP kinase blocked this reaction, which indicates that the PI-3 kinase-p38 MAP kinase pathway is required for this reaction. Inhibition of the p38 MAP kinase pathway resulted in immediate restoration of cell-cell interaction. This result indicates that signaling for adherent molecules is strictly regulated by growth factor signaling. Expression of MUC1 at the cell surface is also observed and found to be expressed only after HRG stimulation. The total amount of MUC1 remains unchanged, suggesting that this amount is not due to induction of gene expression but to translocation of MUC1 from the inner membrane to the plasma membrane. This reaction is independent of the cytohesin pathway but dependent on PI-3 kinase activity. In addition to these reactions, HRG stimulates cell growth of both HCC2998 and MKN45-1 cells, depending on the ERK pathway given that the MEK inhibitor abolishes this effect. Therefore, HRG induces various reactions in HCC2998 and MKN45-1 cells by different pathways. These reactions are all related to characteristics of tumors, which implicates that HRG signaling can contribute to the formation of tumors.
© 2011 Okoshi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in breast cancer cells by the heregulin-beta1-activated p38 signaling pathway enhances endothelial cell migration.Cancer Res. 2001 Feb 15;61(4):1727-32. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11245489
-
Scattering of MCF7 cells by heregulin ß-1 depends on the MEK and p38 MAP kinase pathway.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53298. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053298. Epub 2013 Jan 7. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23308187 Free PMC article.
-
Heregulin-induced VEGF expression via the ErbB3 signaling pathway in colon cancer.Digestion. 2009;80(4):215-25. doi: 10.1159/000229775. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Digestion. 2009. PMID: 19797898
-
Heregulin in breast cancer: old story, new paradigm.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(30):4874-8. doi: 10.2174/1381612819666131125151519. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24283953 Review.
-
Mechanisms behind signet ring cell carcinoma formation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Aug 8;450(4):1231-3. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.07.025. Epub 2014 Jul 11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 25019985 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic and epigenomic analyses explore the potential role of H3K4me3 in neomycin-induced cochlear Lgr5+ progenitor cell regeneration of hair cells.Hum Cell. 2022 Jul;35(4):1030-1044. doi: 10.1007/s13577-022-00727-z. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Hum Cell. 2022. PMID: 35668241
References
-
- Vermeer PD, Einwalter LA, Moninger TO, Rokhlina T, Kern JA, et al. Segregation of receptor and ligand regulates activation of epithelial growth factor receptor. Nature. 2003;422:322–326. - PubMed
-
- Falls DL. Neuregulins: functions, forms, and signaling strategies. Exp Cell Res. 2003;284:14–30. - PubMed
-
- Jones FE, Jerry DJ, Guarino BC, Andrews GC, Stern DF. Heregulin induces in vivo proliferation and differentiation of mammary epithelium into secretory lobuloalveoli. Cell Growth Differ. 1996;7:1031–1038. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

