Circadian clocks in mouse and human CD4+ T cells
- PMID: 22216357
- PMCID: PMC3247291
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029801
Circadian clocks in mouse and human CD4+ T cells
Abstract
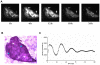
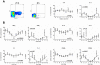
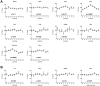
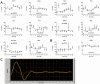
Though it has been shown that immunological functions of CD4+ T cells are time of day-dependent, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain largely obscure. To address the question whether T cells themselves harbor a functional clock driving circadian rhythms of immune function, we analyzed clock gene expression by qPCR in unstimulated CD4+ T cells and immune responses of PMA/ionomycin stimulated CD4+ T cells by FACS analysis purified from blood of healthy subjects at different time points throughout the day. Molecular clock as well as immune function was further analyzed in unstimulated T cells which were cultured in serum-free medium with circadian clock reporter systems. We found robust rhythms of clock gene expression as well as, after stimulation, IL-2, IL-4, IFN-γ production and CD40L expression in freshly isolated CD4+ T cells. Further analysis of IFN-γ and CD40L in cultivated T cells revealed that these parameters remain rhythmic in vitro. Moreover, circadian luciferase reporter activity in CD4+ T cells and in thymic sections from PER2::LUCIFERASE reporter mice suggest that endogenous T cell clock rhythms are self-sustained under constant culture conditions. Microarray analysis of stimulated CD4+ T cell cultures revealed regulation of the NF-κB pathway as a candidate mechanism mediating circadian immune responses. Collectively, these data demonstrate for the first time that CD4+ T cell responses are regulated by an intrinsic cellular circadian oscillator capable of driving rhythmic CD4+ T cell immune responses.
© 2011 Bollinger et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Reppert SM, Weaver DR. Coordination of circadian timing in mammals. Nature. 2002;418:935–941. 10.1038/nature00965 [doi];nature00965 [pii] - PubMed
-
- Toh KL, Jones CR, He Y, Eide EJ, Hinz WA, et al. An hPer2 phosphorylation site mutation in familial advanced sleep phase syndrome. Science. 2001;291:1040–1043. - PubMed
-
- Schibler U, Sassone-Corsi P. A web of circadian pacemakers. Cell. 2002;111:919–922. S0092867402012254 [pii] - PubMed
-
- Balsalobre A, Damiola F, Schibler U. A serum shock induces circadian gene expression in mammalian tissue culture cells. Cell. 1998;93:929–937. S0092-8674(00)81199-X [pii] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

